AutoWeka4MCPS-AVATAR: Accelerating Automated Machine Learning Pipeline Composition and Optimisation
Paper and Code
Nov 21, 2020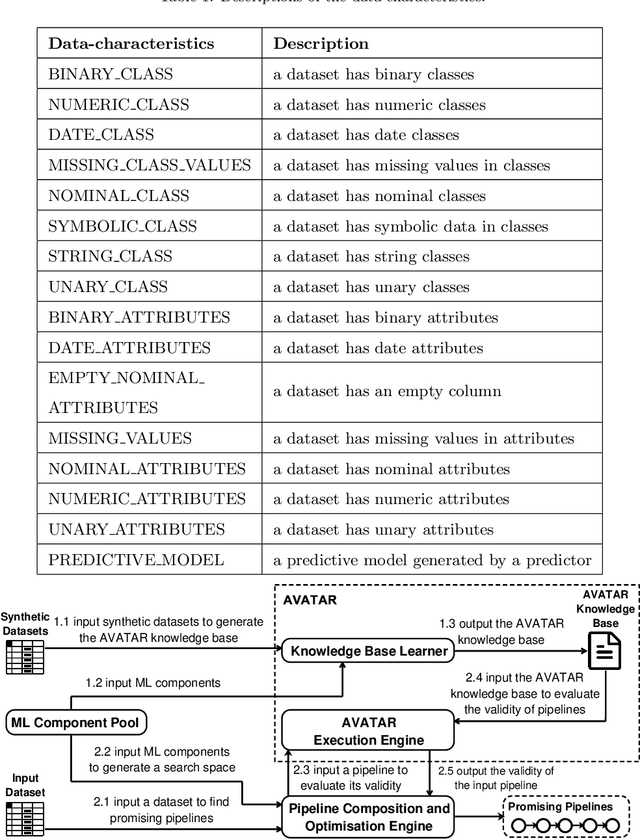
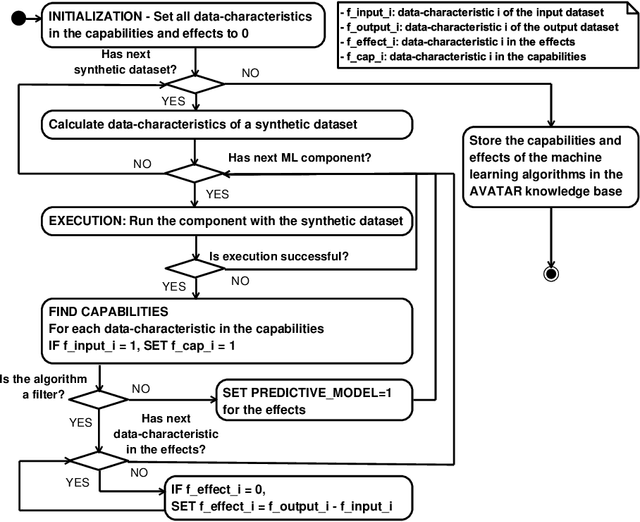
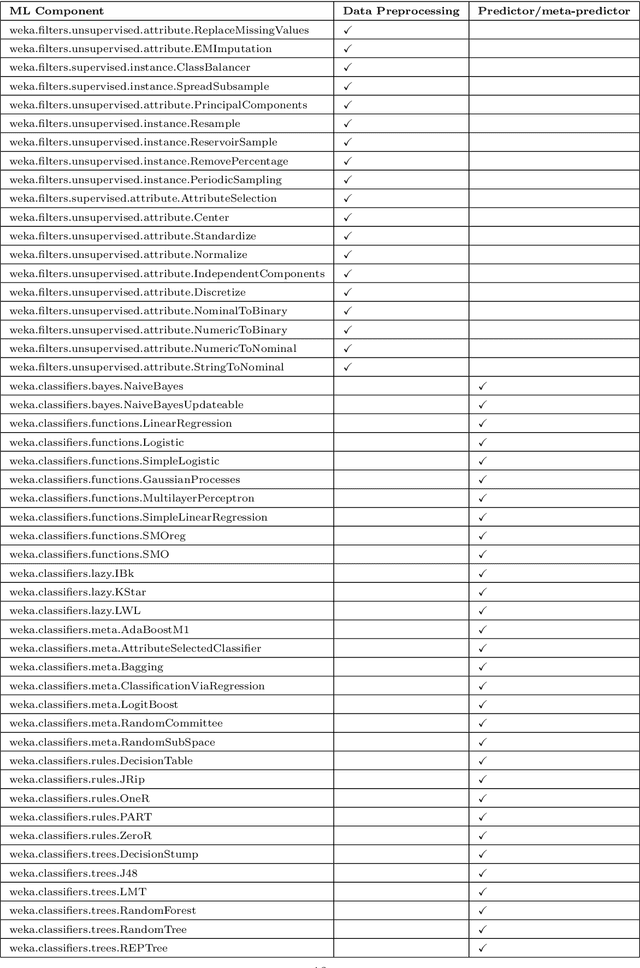
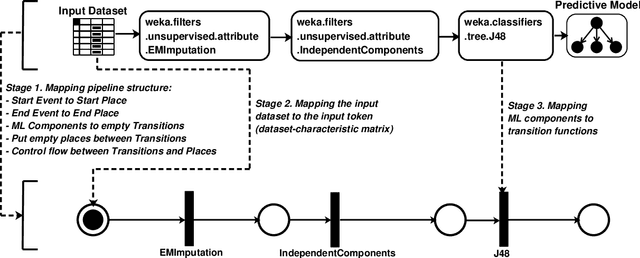
Automated machine learning pipeline (ML) composition and optimisation aim at automating the process of finding the most promising ML pipelines within allocated resources (i.e., time, CPU and memory). Existing methods, such as Bayesian-based and genetic-based optimisation, which are implemented in Auto-Weka, Auto-sklearn and TPOT, evaluate pipelines by executing them. Therefore, the pipeline composition and optimisation of these methods frequently require a tremendous amount of time that prevents them from exploring complex pipelines to find better predictive models. To further explore this research challenge, we have conducted experiments showing that many of the generated pipelines are invalid in the first place, and attempting to execute them is a waste of time and resources. To address this issue, we propose a novel method to evaluate the validity of ML pipelines, without their execution, using a surrogate model (AVATAR). The AVATAR generates a knowledge base by automatically learning the capabilities and effects of ML algorithms on datasets' characteristics. This knowledge base is used for a simplified mapping from an original ML pipeline to a surrogate model which is a Petri net based pipeline. Instead of executing the original ML pipeline to evaluate its validity, the AVATAR evaluates its surrogate model constructed by capabilities and effects of the ML pipeline components and input/output simplified mappings. Evaluating this surrogate model is less resource-intensive than the execution of the original pipeline. As a result, the AVATAR enables the pipeline composition and optimisation methods to evaluate more pipelines by quickly rejecting invalid pipelines. We integrate the AVATAR into the sequential model-based algorithm configuration (SMAC). Our experiments show that when SMAC employs AVATAR, it finds better solutions than on its own.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge