Automatic phantom test pattern classification through transfer learning with deep neural networks
Paper and Code
Jan 22, 2020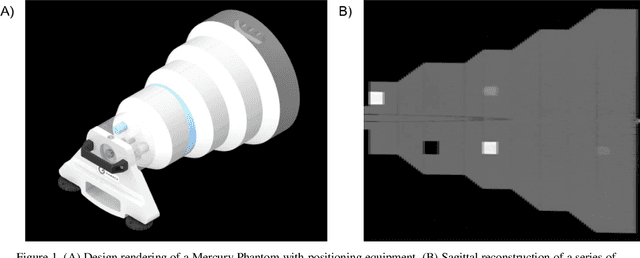
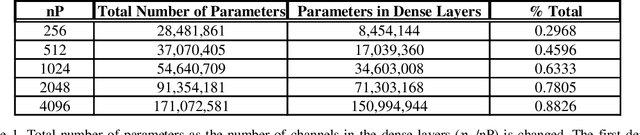
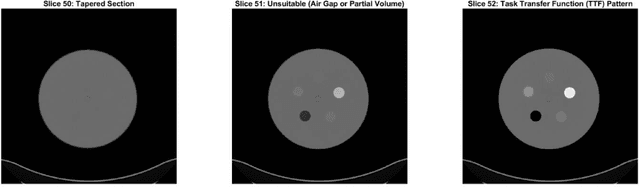
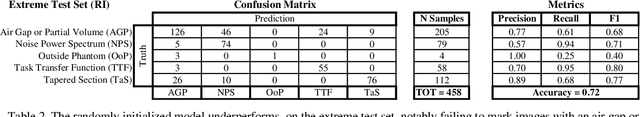
Imaging phantoms are test patterns used to measure image quality in computer tomography (CT) systems. A new phantom platform (Mercury Phantom, Gammex) provides test patterns for estimating the task transfer function (TTF) or noise power spectrum (NPF) and simulates different patient sizes. Determining which image slices are suitable for analysis currently requires manual annotation of these patterns by an expert, as subtle defects may make an image unsuitable for measurement. We propose a method of automatically classifying these test patterns in a series of phantom images using deep learning techniques. By adapting a convolutional neural network based on the VGG19 architecture with weights trained on ImageNet, we use transfer learning to produce a classifier for this domain. The classifier is trained and evaluated with over 3,500 phantom images acquired at a university medical center. Input channels for color images are successfully adapted to convey contextual information for phantom images. A series of ablation studies are employed to verify design aspects of the classifier and evaluate its performance under varying training conditions. Our solution makes extensive use of image augmentation to produce a classifier that accurately classifies typical phantom images with 98% accuracy, while maintaining as much as 86% accuracy when the phantom is improperly imaged.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge