Automated Aerial Animal Detection When Spatial Resolution Conditions Are Varied
Paper and Code
Oct 04, 2021
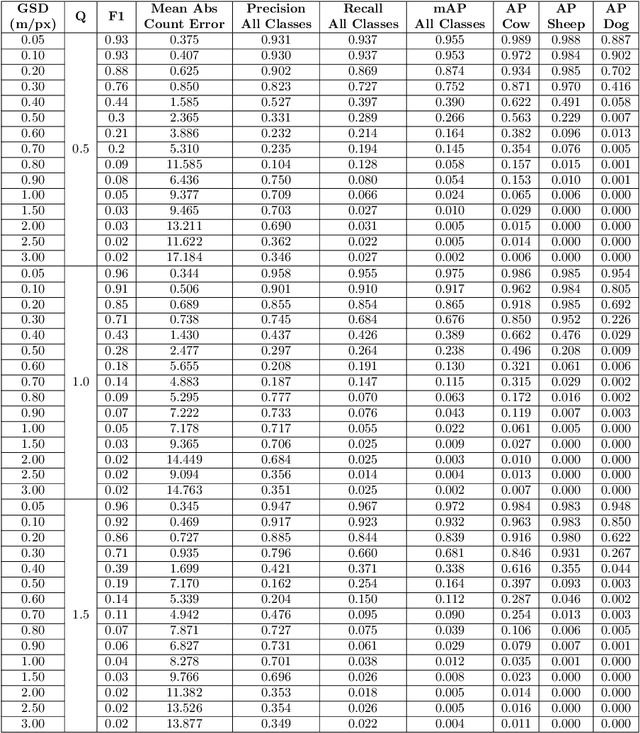
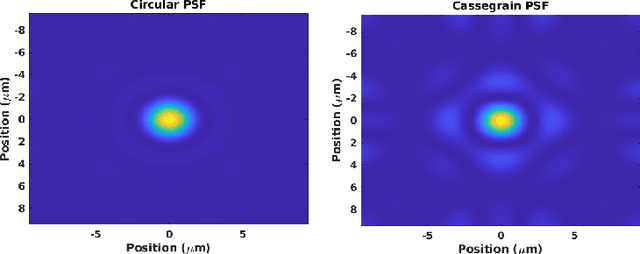
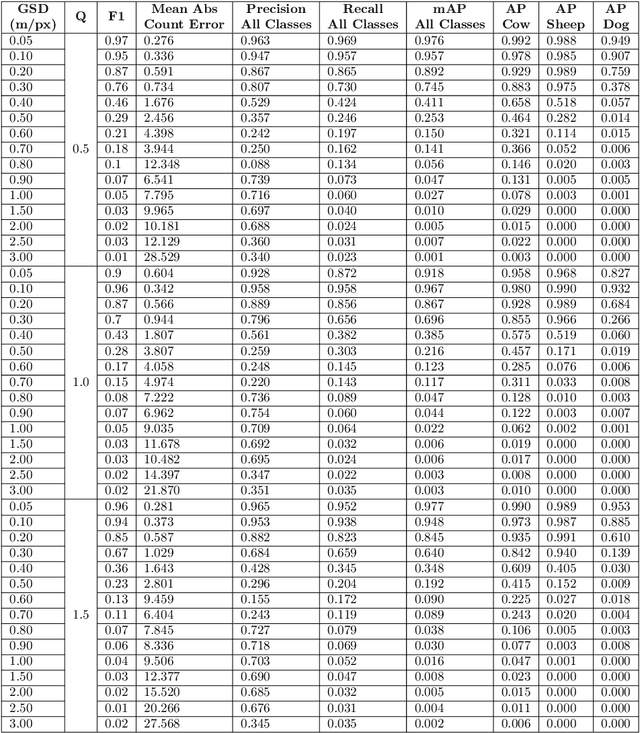
Knowing where livestock are located enables optimized management and mustering. However, Australian farms are large meaning that many of Australia's livestock are unmonitored which impacts farm profit, animal welfare and the environment. Effective animal localisation and counting by analysing satellite imagery overcomes this management hurdle however, high resolution satellite imagery is expensive. Thus, to minimise cost the lowest spatial resolution data that enables accurate livestock detection should be selected. In our work, we determine the association between object detector performance and spatial degradation for cattle, sheep and dogs. Accurate ground truth was established using high resolution drone images which were then downsampled to various ground sample distances (GSDs). Both circular and cassegrain aperture optics were simulated to generate point spread functions (PSFs) corresponding to various optical qualities. By simulating the PSF, rather than approximating it as a Gaussian, the images were accurately degraded to match the spatial resolution and blurring structure of satellite imagery. Two existing datasets were combined and used to train and test a YoloV5 object detection network. Detector performance was found to drop steeply around a GSD of 0.5m/px and was associated with PSF matrix structure within this GSD region. Detector mAP performance fell by 52 percent when a cassegrain, rather than circular, aperture was used at a 0.5m/px GSD. Overall blurring magnitude also had a small impact when matched to GSD, as did the internal network resolution. Our results here inform the selection of remote sensing data requirements for animal detection tasks, allowing farmers and ecologists to use more accessible medium resolution imagery with confidence.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge