Approximate Query Processing using Deep Generative Models
Paper and Code
Mar 24, 2019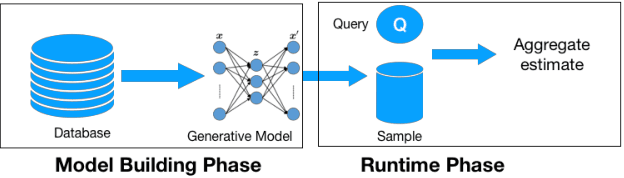

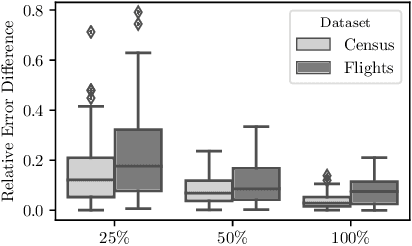

Data is generated at an unprecedented rate surpassing our ability to analyze them. One viable solution that was pioneered by the database community is Approximate Query Processing (AQP). AQP seeks to provide approximate answers to queries in a fraction of time needed for computing exact answers. This is often achieved by running the query on a pre-computed or on-demand derived sample and generating estimates for the entire dataset based on the result. In this work, we explore a novel approach for AQP utilizing deep learning (DL). We use deep generative models, an unsupervised learning based approach, to learn the data distribution faithfully in a compact manner (typically few hundred KBs). Queries could be answered approximately by generating samples from the learned model. This approach eliminates the dependency of AQP to a sample of fixed size and allows us to satisfy arbitrary accuracy requirements by generating as many samples as needed very fast. While we specifically focus on variational autoencoders (VAE), we demonstrate how our approach could also be used for other popular DL models such as generative adversarial networks (GAN) and deep Bayesian networks (DBN). Our other contributions include (a) identifying model bias and minimizing it through a rejection sampling based approach (b) An algorithm to build model ensembles for AQP for improved accuracy and (c) an analysis of VAE latent space to understand its suitability to AQP. Our extensive experiments show that deep learning is a very promising approach for AQP.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge