Anatomy-informed Data Augmentation for Enhanced Prostate Cancer Detection
Paper and Code
Sep 07, 2023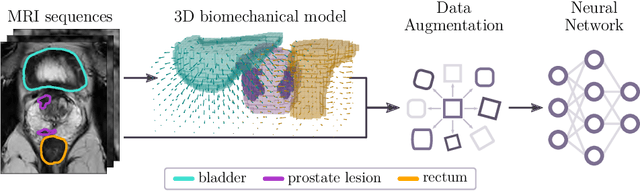

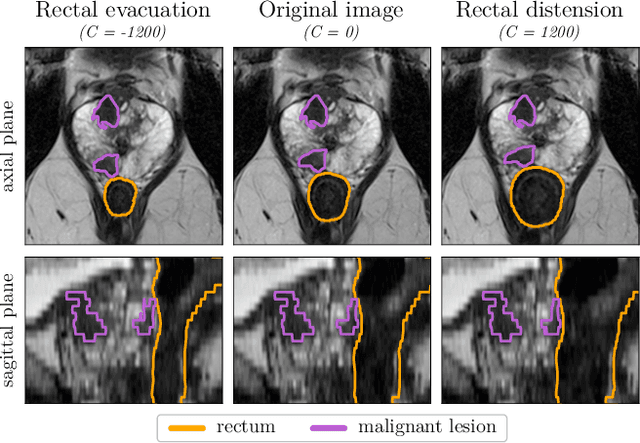
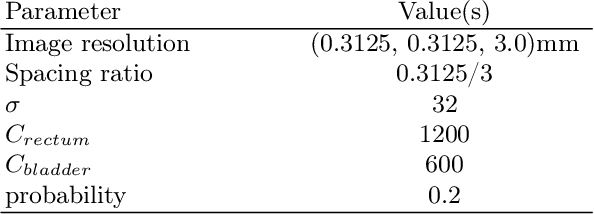
Data augmentation (DA) is a key factor in medical image analysis, such as in prostate cancer (PCa) detection on magnetic resonance images. State-of-the-art computer-aided diagnosis systems still rely on simplistic spatial transformations to preserve the pathological label post transformation. However, such augmentations do not substantially increase the organ as well as tumor shape variability in the training set, limiting the model's ability to generalize to unseen cases with more diverse localized soft-tissue deformations. We propose a new anatomy-informed transformation that leverages information from adjacent organs to simulate typical physiological deformations of the prostate and generates unique lesion shapes without altering their label. Due to its lightweight computational requirements, it can be easily integrated into common DA frameworks. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our augmentation on a dataset of 774 biopsy-confirmed examinations, by evaluating a state-of-the-art method for PCa detection with different augmentation settings.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge