Analysis of Neural Video Compression Networks for 360-Degree Video Coding
Paper and Code
Feb 15, 2024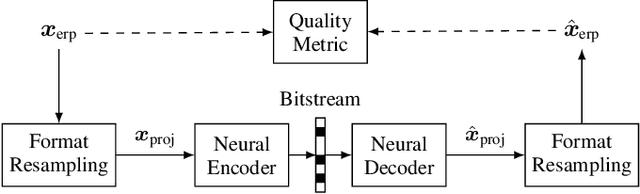
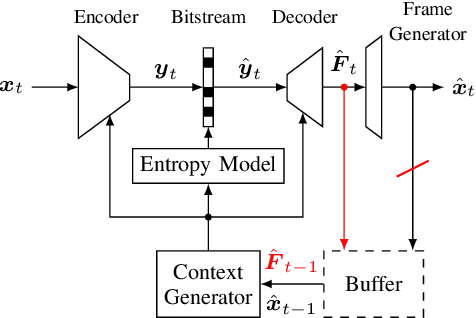
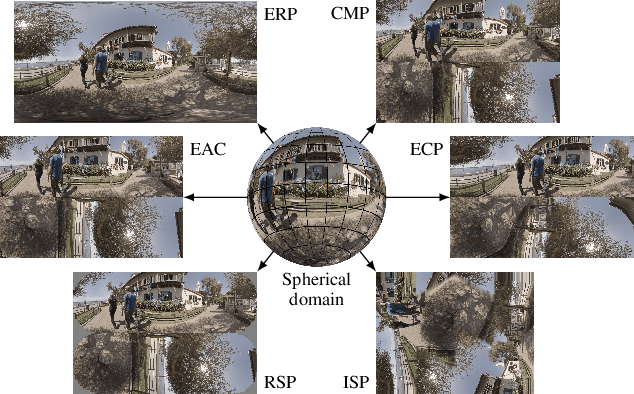
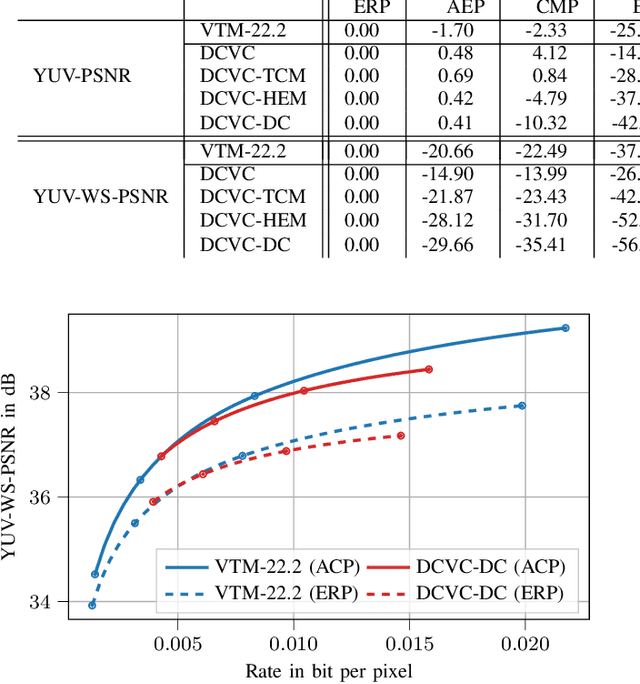
With the increasing efforts of bringing high-quality virtual reality technologies into the market, efficient 360-degree video compression gains in importance. As such, the state-of-the-art H.266/VVC video coding standard integrates dedicated tools for 360-degree video, and considerable efforts have been put into designing 360-degree projection formats with improved compression efficiency. For the fast-evolving field of neural video compression networks (NVCs), the effects of different 360-degree projection formats on the overall compression performance have not yet been investigated. It is thus unclear, whether a resampling from the conventional equirectangular projection (ERP) to other projection formats yields similar gains for NVCs as for hybrid video codecs, and which formats perform best. In this paper, we analyze several generations of NVCs and an extensive set of 360-degree projection formats with respect to their compression performance for 360-degree video. Based on our analysis, we find that projection format resampling yields significant improvements in compression performance also for NVCs. The adjusted cubemap projection (ACP) and equatorial cylindrical projection (ECP) show to perform best and achieve rate savings of more than 55% compared to ERP based on WS-PSNR for the most recent NVC. Remarkably, the observed rate savings are higher than for H.266/VVC, emphasizing the importance of projection format resampling for NVCs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge