Analysis of Executional and Procedural Errors in Dry-lab Robotic Surgery Experiments
Paper and Code
Jun 22, 2021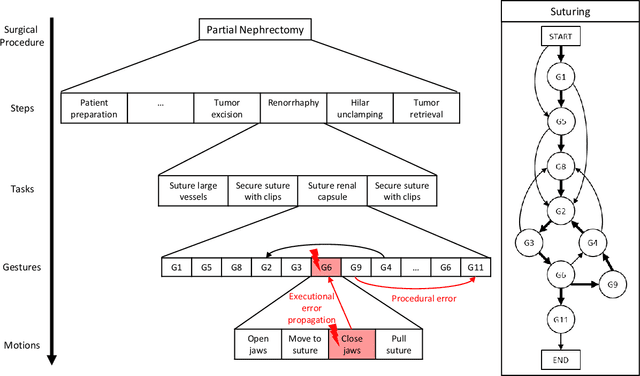
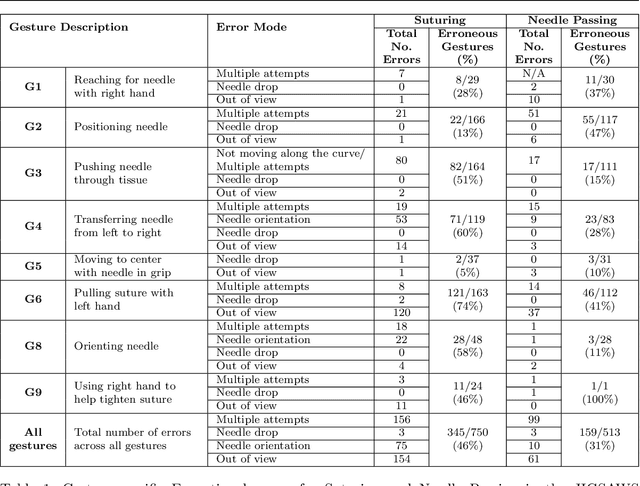
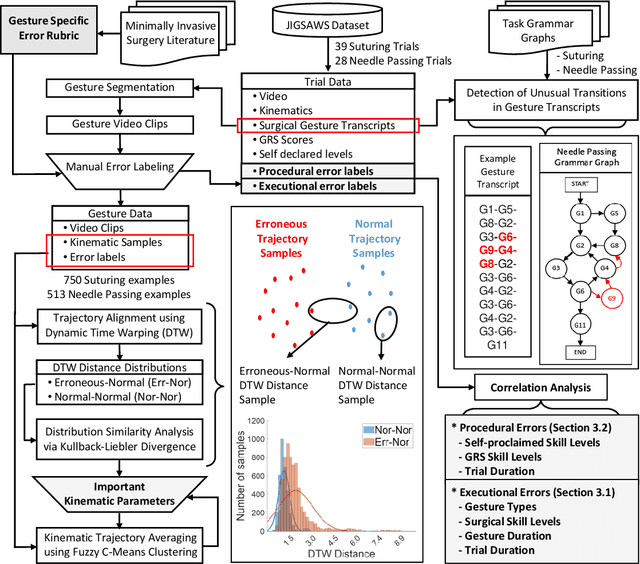
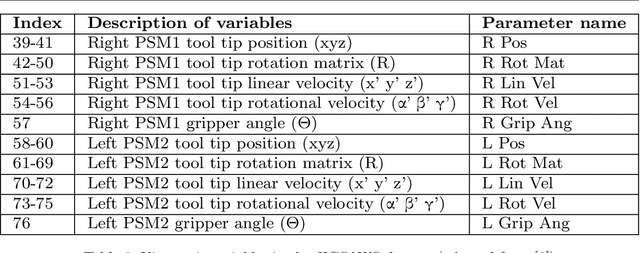
Background We aim to develop a method for automated detection of potentially erroneous motions that lead to sub-optimal surgeon performance and safety-critical events in robot-assisted surgery. Methods We develop a rubric for identifying task and gesture-specific Executional and Procedural errors and evaluate dry-lab demonstrations of Suturing and Needle Passing tasks from the JIGSAWS dataset. We characterize erroneous parts of demonstrations by labeling video data, and use distribution similarity analysis and trajectory averaging on kinematic data to identify parameters that distinguish erroneous gestures. Results Executional error frequency varies by task and gesture and correlates with skill level. Some predominant error modes in each gesture are distinguishable by analyzing error-specific kinematic parameters. Procedural errors could lead to lower performance scores and increased demonstration times but also depend on surgical style. Conclusions This study provides preliminary evidence that automated error detection can provide context-dependent and quantitative feedback to surgical trainees for performance improvement.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge