Analogical Reasoning Inside Large Language Models: Concept Vectors and the Limits of Abstraction
Paper and Code
Mar 05, 2025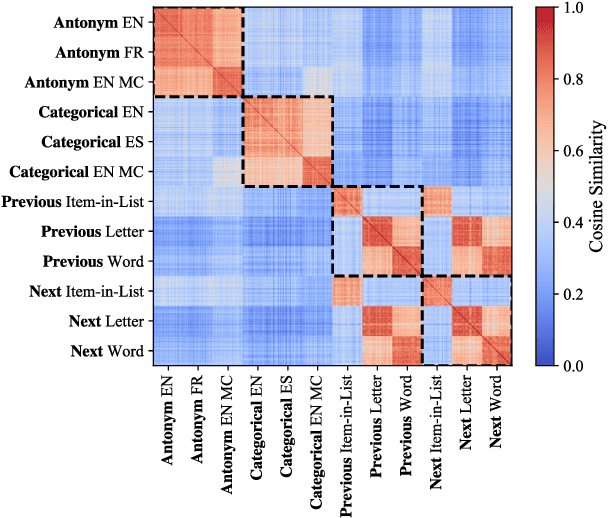
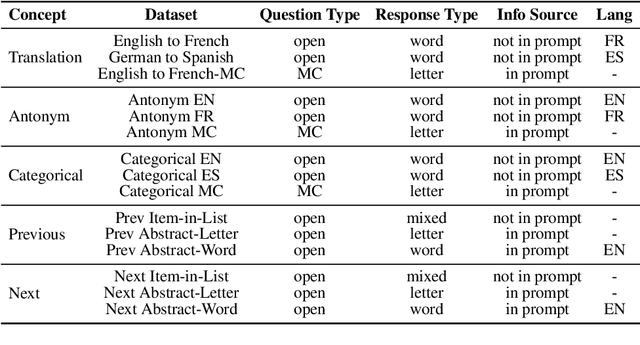
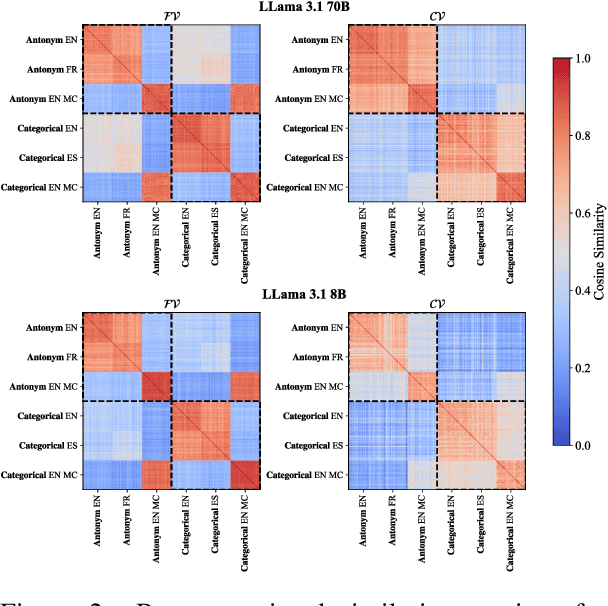
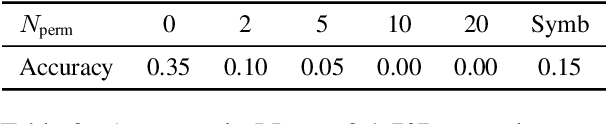
Analogical reasoning relies on conceptual abstractions, but it is unclear whether Large Language Models (LLMs) harbor such internal representations. We explore distilled representations from LLM activations and find that function vectors (FVs; Todd et al., 2024) - compact representations for in-context learning (ICL) tasks - are not invariant to simple input changes (e.g., open-ended vs. multiple-choice), suggesting they capture more than pure concepts. Using representational similarity analysis (RSA), we localize a small set of attention heads that encode invariant concept vectors (CVs) for verbal concepts like "antonym". These CVs function as feature detectors that operate independently of the final output - meaning that a model may form a correct internal representation yet still produce an incorrect output. Furthermore, CVs can be used to causally guide model behaviour. However, for more abstract concepts like "previous" and "next", we do not observe invariant linear representations, a finding we link to generalizability issues LLMs display within these domains.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge