An Overview of In-memory Processing with Emerging Non-volatile Memory for Data-intensive Applications
Paper and Code
Jun 15, 2019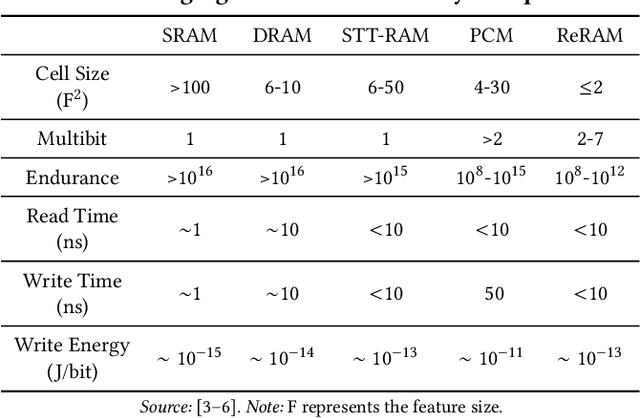
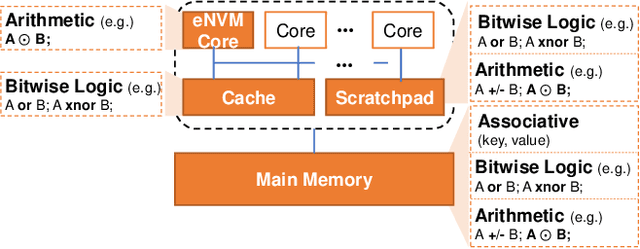
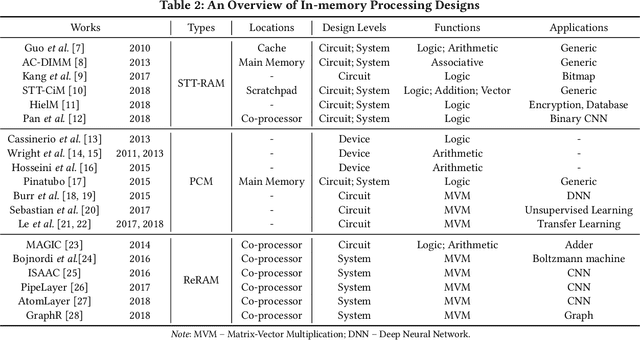
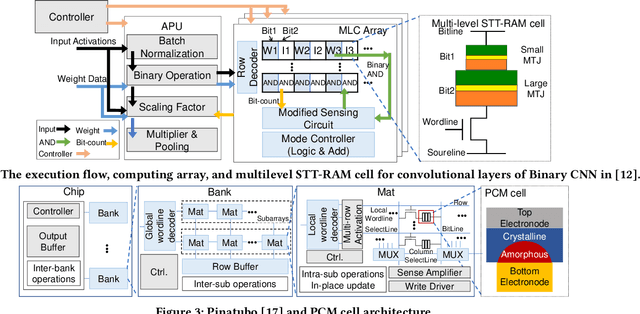
The conventional von Neumann architecture has been revealed as a major performance and energy bottleneck for rising data-intensive applications. %, due to the intensive data movements. The decade-old idea of leveraging in-memory processing to eliminate substantial data movements has returned and led extensive research activities. The effectiveness of in-memory processing heavily relies on memory scalability, which cannot be satisfied by traditional memory technologies. Emerging non-volatile memories (eNVMs) that pose appealing qualities such as excellent scaling and low energy consumption, on the other hand, have been heavily investigated and explored for realizing in-memory processing architecture. In this paper, we summarize the recent research progress in eNVM-based in-memory processing from various aspects, including the adopted memory technologies, locations of the in-memory processing in the system, supported arithmetics, as well as applied applications.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge