An Optimization Based Control Framework for Balancing and Walking: Implementation on the iCub Robot
Paper and Code
Jul 26, 2017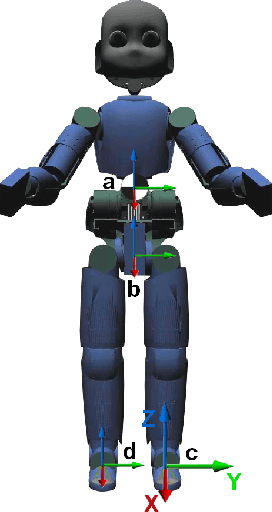
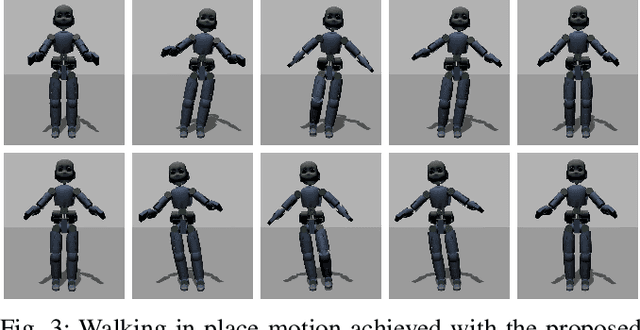
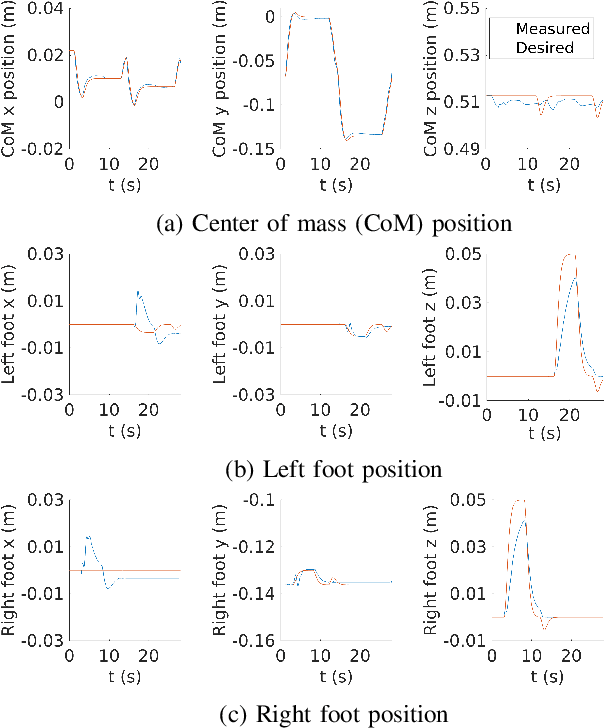
A whole-body torque control framework adapted for balancing and walking tasks is presented in this paper. In the proposed approach, centroidal momentum terms are excluded in favor of a hierarchy of high-priority position and orientation tasks and a low-priority postural task. More specifically, the controller stabilizes the position of the center of mass, the orientation of the pelvis frame, as well as the position and orientation of the feet frames. The low-priority postural task provides reference positions for each joint of the robot. Joint torques and contact forces to stabilize tasks are obtained through quadratic programming optimization. Besides the exclusion of centroidal momentum terms, part of the novelty of the approach lies in the definition of control laws in SE(3) which do not require the use of Euler parameterization. Validation of the framework was achieved in a scenario where the robot kept balance while walking in place. Experiments have been conducted with the iCub robot, in simulation and in real-world experiments.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge