An LSTM Feature Imitation Network for Hand Movement Recognition from sEMG Signals
Paper and Code
May 23, 2024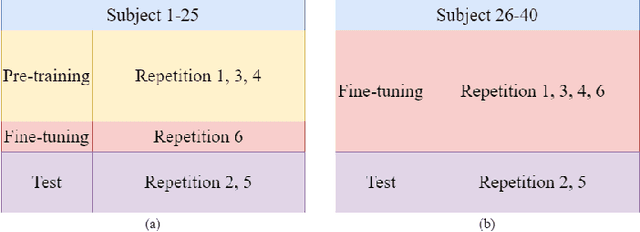
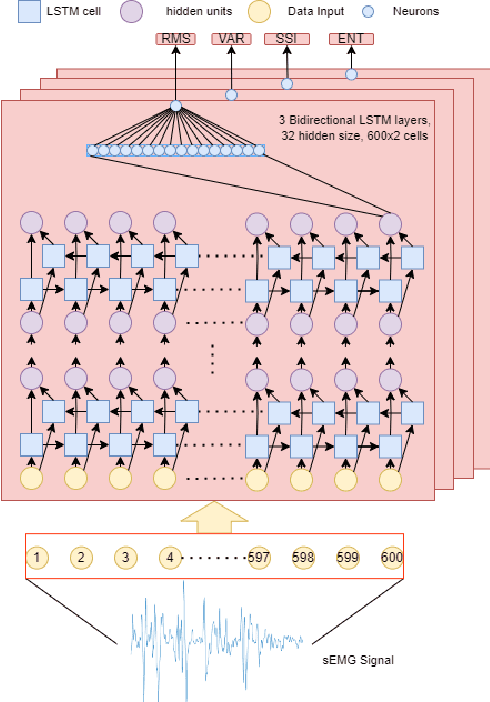
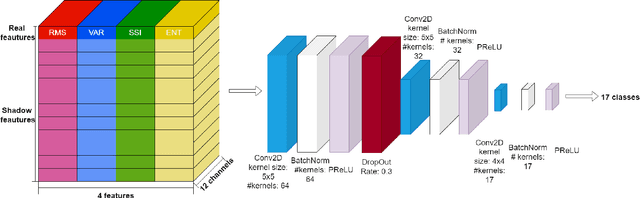
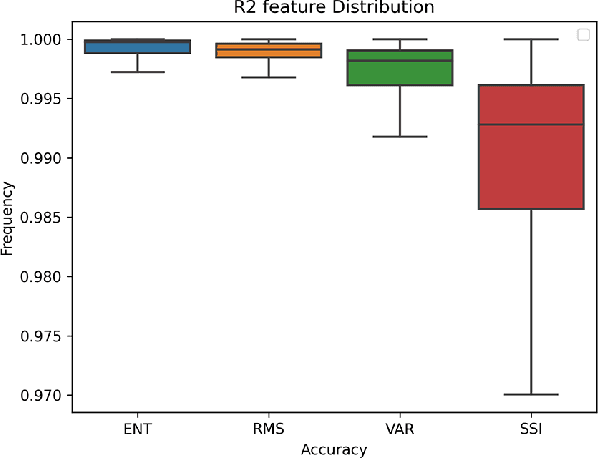
Surface Electromyography (sEMG) is a non-invasive signal that is used in the recognition of hand movement patterns, the diagnosis of diseases, and the robust control of prostheses. Despite the remarkable success of recent end-to-end Deep Learning approaches, they are still limited by the need for large amounts of labeled data. To alleviate the requirement for big data, researchers utilize Feature Engineering, which involves decomposing the sEMG signal into several spatial, temporal, and frequency features. In this paper, we propose utilizing a feature-imitating network (FIN) for closed-form temporal feature learning over a 300ms signal window on Ninapro DB2, and applying it to the task of 17 hand movement recognition. We implement a lightweight LSTM-FIN network to imitate four standard temporal features (entropy, root mean square, variance, simple square integral). We then explore transfer learning capabilities by applying the pre-trained LSTM-FIN for tuning to a downstream hand movement recognition task. We observed that the LSTM network can achieve up to 99\% R2 accuracy in feature reconstruction and 80\% accuracy in hand movement recognition. Our results also showed that the model can be robustly applied for both within- and cross-subject movement recognition, as well as simulated low-latency environments. Overall, our work demonstrates the potential of the FIN modeling paradigm in data-scarce scenarios for sEMG signal processing.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge