An Iterative Spanning Forest Framework for Superpixel Segmentation
Paper and Code
Jan 30, 2018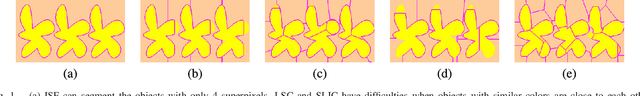
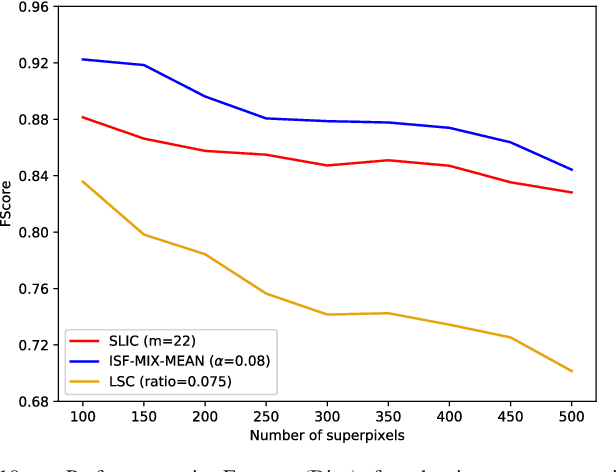
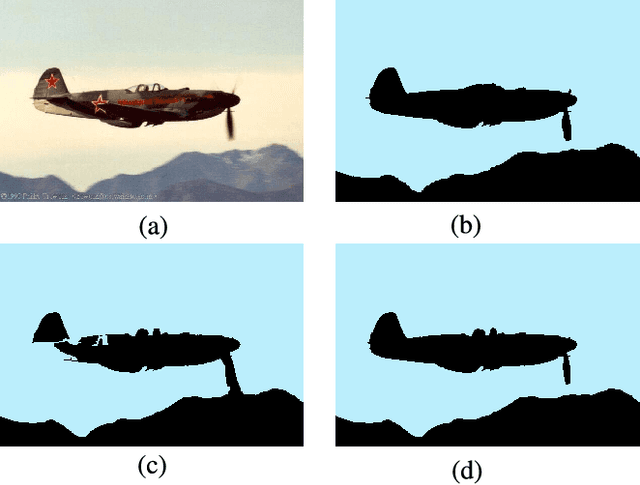

Superpixel segmentation has become an important research problem in image processing. In this paper, we propose an Iterative Spanning Forest (ISF) framework, based on sequences of Image Foresting Transforms, where one can choose i) a seed sampling strategy, ii) a connectivity function, iii) an adjacency relation, and iv) a seed pixel recomputation procedure to generate improved sets of connected superpixels (supervoxels in 3D) per iteration. The superpixels in ISF structurally correspond to spanning trees rooted at those seeds. We present five ISF methods to illustrate different choices of its components. These methods are compared with approaches from the state-of-the-art in effectiveness and efficiency. The experiments involve 2D and 3D datasets with distinct characteristics, and a high level application, named sky image segmentation. The theoretical properties of ISF are demonstrated in the supplementary material and the results show that some of its methods are competitive with or superior to the best baselines in effectiveness and efficiency.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge