An Investigation of Monotonic Transducers for Large-Scale Automatic Speech Recognition
Paper and Code
Apr 19, 2022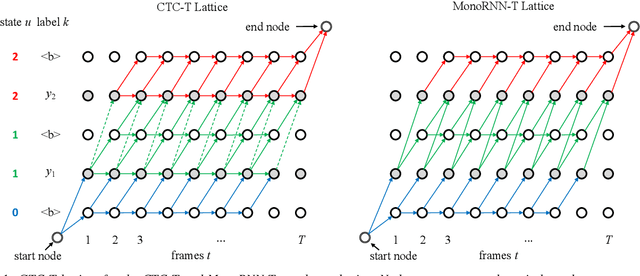
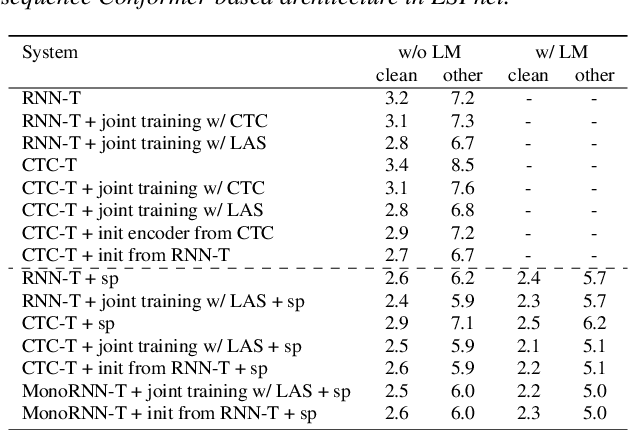
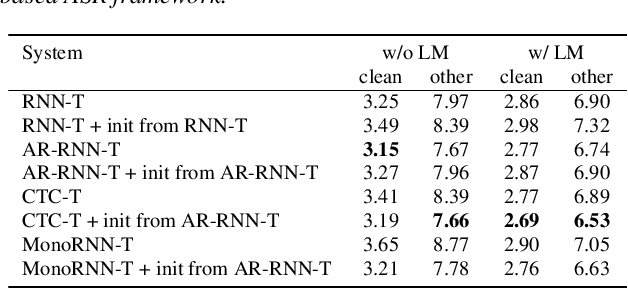
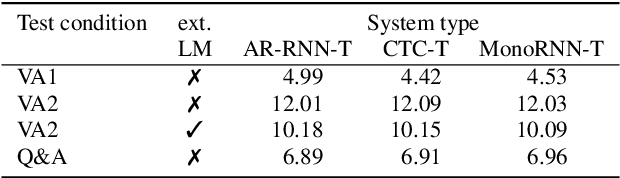
The two most popular loss functions for streaming end-to-end automatic speech recognition (ASR) are the RNN-Transducer (RNN-T) and the connectionist temporal classification (CTC) objectives. Both perform an alignment-free training by marginalizing over all possible alignments, but use different transition rules. Between these two loss types we can classify the monotonic RNN-T (MonoRNN-T) and the recently proposed CTC-like Transducer (CTC-T), which both can be realized using the graph temporal classification-transducer (GTC-T) loss function. Monotonic transducers have a few advantages. First, RNN-T can suffer from runaway hallucination, where a model keeps emitting non-blank symbols without advancing in time, often in an infinite loop. Secondly, monotonic transducers consume exactly one model score per time step and are therefore more compatible and unifiable with traditional FST-based hybrid ASR decoders. However, the MonoRNN-T so far has been found to have worse accuracy than RNN-T. It does not have to be that way, though: By regularizing the training - via joint LAS training or parameter initialization from RNN-T - both MonoRNN-T and CTC-T perform as well - or better - than RNN-T. This is demonstrated for LibriSpeech and for a large-scale in-house data set.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge