An Evaluation Study of Intrinsic Motivation Techniques applied to Reinforcement Learning over Hard Exploration Environments
Paper and Code
May 23, 2022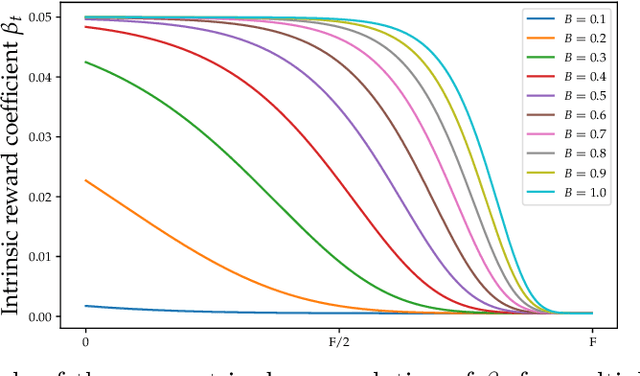
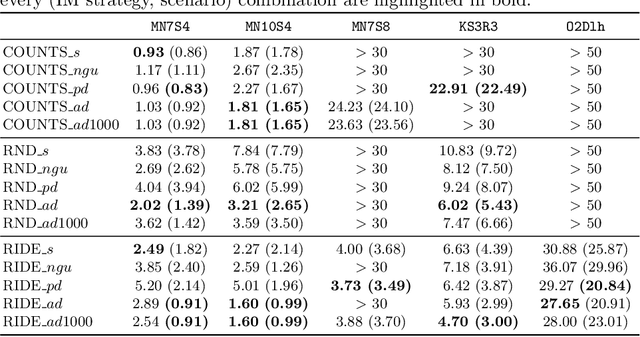
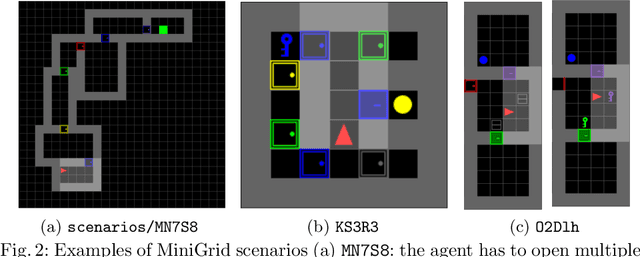
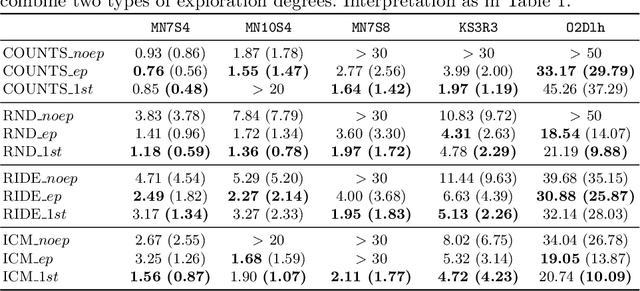
In the last few years, the research activity around reinforcement learning tasks formulated over environments with sparse rewards has been especially notable. Among the numerous approaches proposed to deal with these hard exploration problems, intrinsic motivation mechanisms are arguably among the most studied alternatives to date. Advances reported in this area over time have tackled the exploration issue by proposing new algorithmic ideas to generate alternative mechanisms to measure the novelty. However, most efforts in this direction have overlooked the influence of different design choices and parameter settings that have also been introduced to improve the effect of the generated intrinsic bonus, forgetting the application of those choices to other intrinsic motivation techniques that may also benefit of them. Furthermore, some of those intrinsic methods are applied with different base reinforcement algorithms (e.g. PPO, IMPALA) and neural network architectures, being hard to fairly compare the provided results and the actual progress provided by each solution. The goal of this work is to stress on this crucial matter in reinforcement learning over hard exploration environments, exposing the variability and susceptibility of avant-garde intrinsic motivation techniques to diverse design factors. Ultimately, our experiments herein reported underscore the importance of a careful selection of these design aspects coupled with the exploration requirements of the environment and the task in question under the same setup, so that fair comparisons can be guaranteed.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge