An AI based Digital Score of Tumour-Immune Microenvironment Predicts Benefit to Maintenance Immunotherapy in Advanced Oesophagogastric Adenocarcinoma
Paper and Code
Feb 29, 2024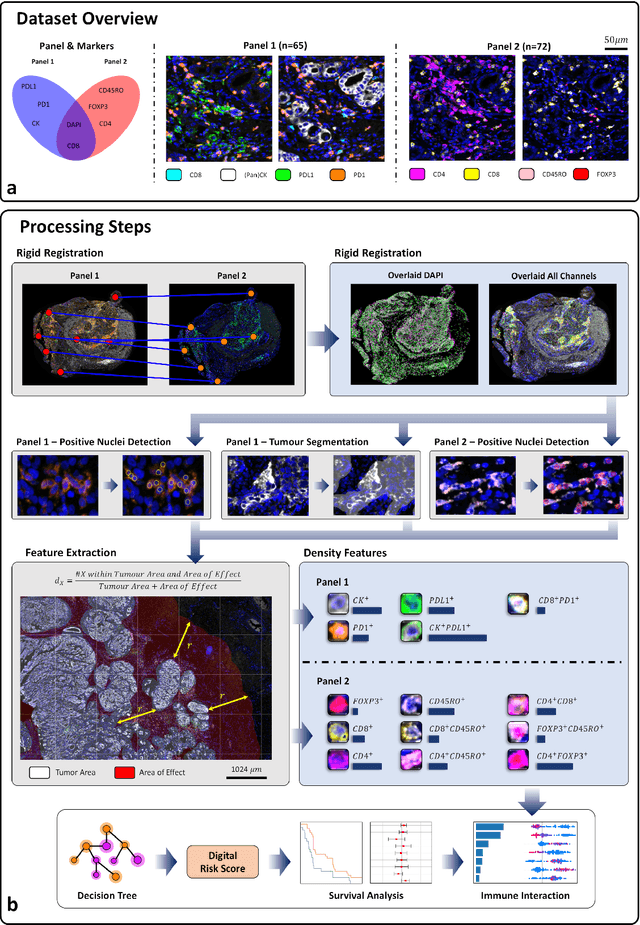
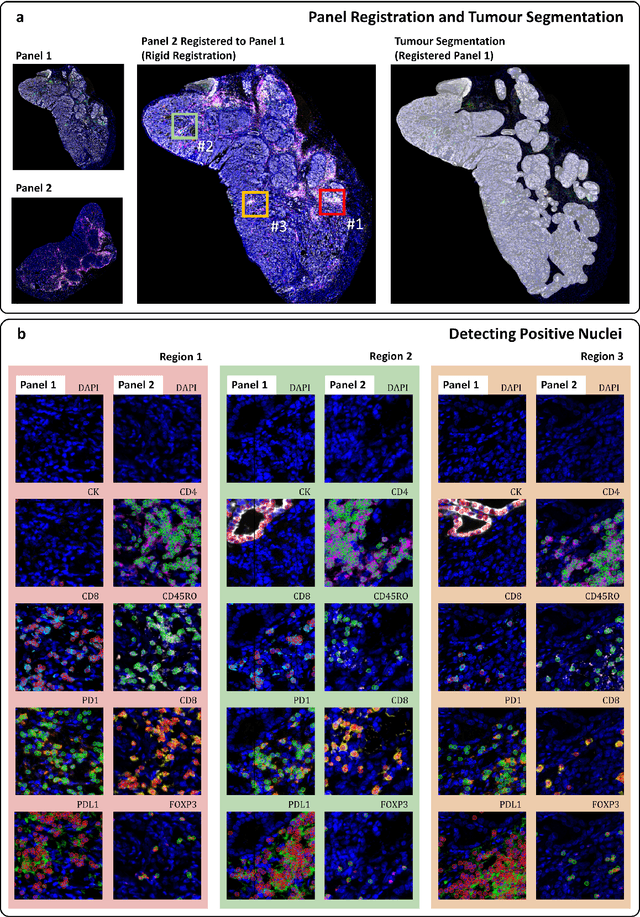
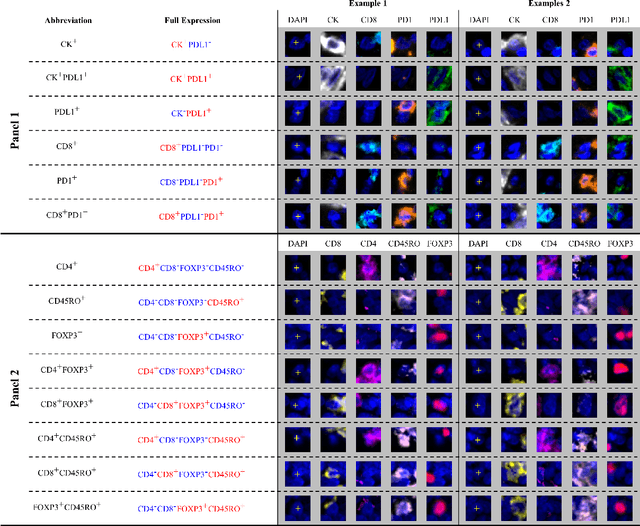
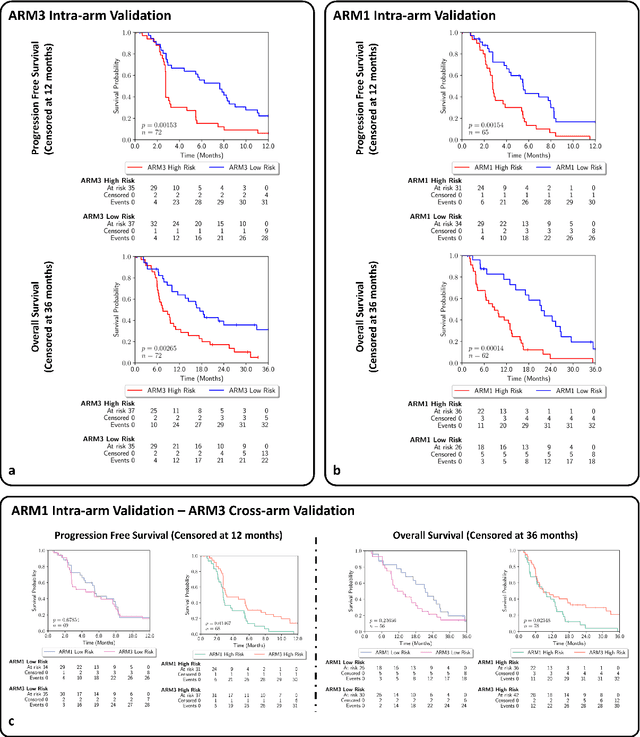
Gastric and oesophageal (OG) cancers are the leading causes of cancer mortality worldwide. In OG cancers, recent studies have showed that PDL1 immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICI) in combination with chemotherapy improves patient survival. However, our understanding of the tumour immune microenvironment in OG cancers remains limited. In this study, we interrogate multiplex immunofluorescence (mIF) images taken from patients with advanced Oesophagogastric Adenocarcinoma (OGA) who received first-line fluoropyrimidine and platinum-based chemotherapy in the PLATFORM trial (NCT02678182) to predict the efficacy of the treatment and to explore the biological basis of patients responding to maintenance durvalumab (PDL1 inhibitor). Our proposed Artificial Intelligence (AI) based marker successfully identified responder from non-responder (p < 0.05) as well as those who could potentially benefit from ICI with statistical significance (p < 0.05) for both progression free and overall survival. Our findings suggest that T cells that express FOXP3 seem to heavily influence the patient treatment response and survival outcome. We also observed that higher levels of CD8+PD1+ cells are consistently linked to poor prognosis for both OS and PFS, regardless of ICI.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge