An Affective Robot Companion for Assisting the Elderly in a Cognitive Game Scenario
Paper and Code
Jul 12, 2018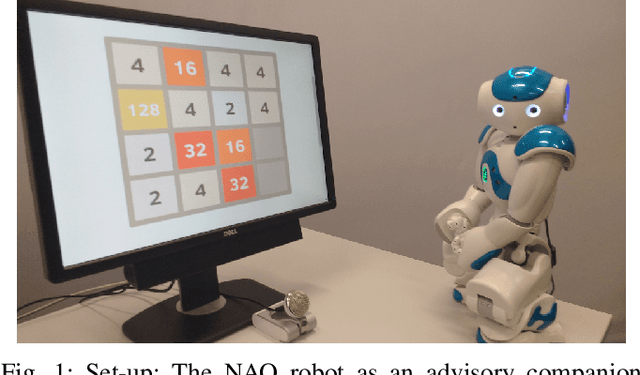
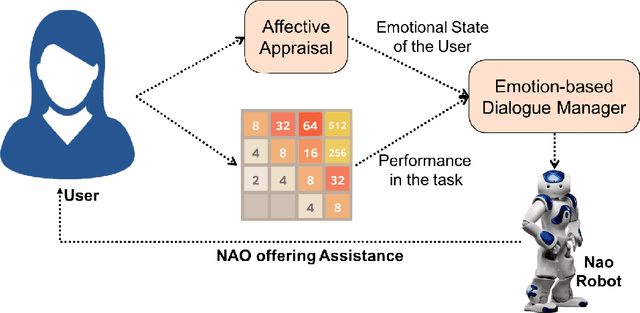
Being able to recognize emotions in human users is considered a highly desirable trait in Human-Robot Interaction (HRI) scenarios. However, most contemporary approaches rarely attempt to apply recognized emotional features in an active manner to modulate robot decision-making and dialogue for the benefit of the user. In this position paper, we propose a method of incorporating recognized emotions into a Reinforcement Learning (RL) based dialogue management module that adapts its dialogue responses in order to attempt to make cognitive training tasks, like the 2048 Puzzle Game, more enjoyable for the users.
* Proceedings of the Workshop on Intelligent Assistive Computing, IEEE
World Congress on Computational Intelligence (WCCI) 2018
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge