Amur Tiger Re-identification in the Wild
Paper and Code
Jun 14, 2019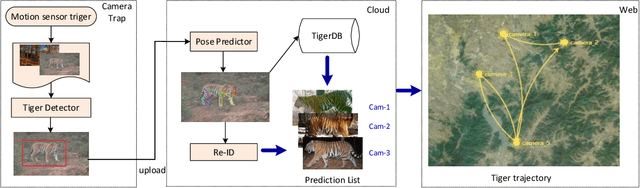
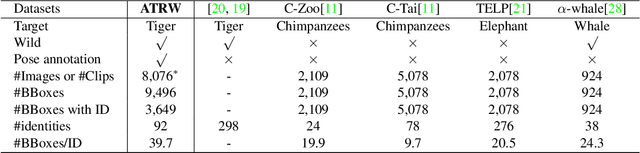
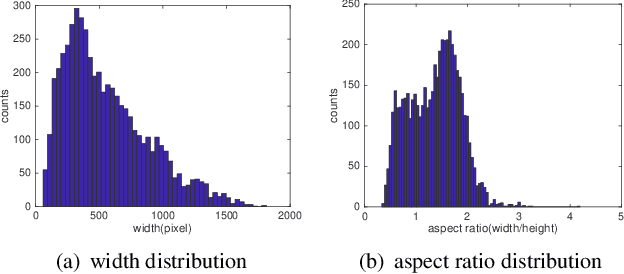
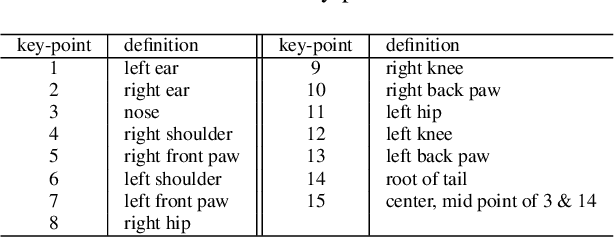
Monitoring the population and movements of endangered species is an important task to wildlife conversation. Traditional tagging methods do not scale to large populations, while applying computer vision methods to camera sensor data requires re-identification (re-ID) algorithms to obtain accurate counts and moving trajectory of wildlife. However, existing re-ID methods are largely targeted at persons and cars, which have limited pose variations and constrained capture environments. This paper tries to fill the gap by introducing a novel large-scale dataset, the Amur Tiger Re-identification in the Wild (ATRW) dataset. ATRW contains over 8,000 video clips from 92 Amur tigers, with bounding box, pose keypoint, and tiger identity annotations. In contrast to typical re-ID datasets, the tigers are captured in a diverse set of unconstrained poses and lighting conditions. We demonstrate with a set of baseline algorithms that ATRW is a challenging dataset for re-ID. Lastly, we propose a novel method for tiger re-identification, which introduces precise pose parts modeling in deep neural networks to handle large pose variation of tigers, and reaches notable performance improvement over existing re-ID methods. The dataset will be public available at https://cvwc2019.github.io/ .
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge