AMR Alignment: Paying Attention to Cross-Attention
Paper and Code
Jun 15, 2022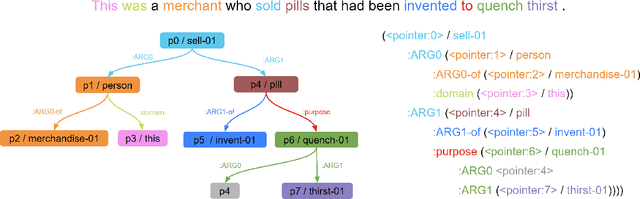
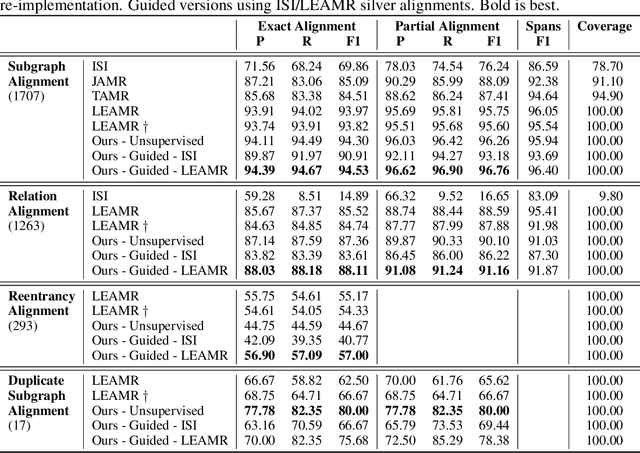

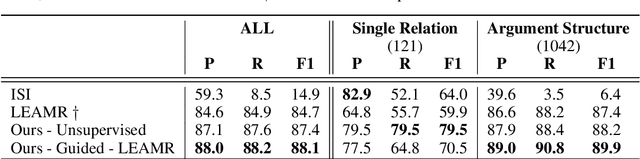
With the surge of Transformer models, many have investigated how attention acts on the learned representations. However, attention is still overlooked for specific tasks, such as Semantic Parsing. A popular approach to the formal representation of a sentence's meaning is Abstract Meaning Representation (AMR). Until now, the alignment between a sentence and its AMR representation has been explored in different ways, such as through rules or via the Expectation Maximization (EM) algorithm. In this paper, we investigate the ability of Transformer-based parsing models to yield effective alignments without ad-hoc strategies. We present the first in-depth exploration of cross-attention for AMR by proxy of alignment between the sentence spans and the semantic units in the graph. We show how current Transformer-based parsers implicitly encode the alignment information in the cross-attention weights and how to leverage it to extract such alignment. Furthermore, we supervise and guide cross-attention using alignment, dropping the need for English- and AMR-specific rules.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge