AmicroN: A Framework for Generating Annotations for Human Activity Recognition with Granular Micro-Activities
Paper and Code
Jun 22, 2023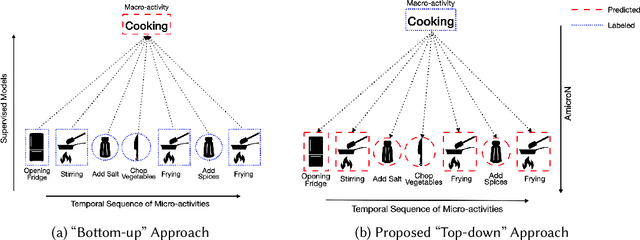
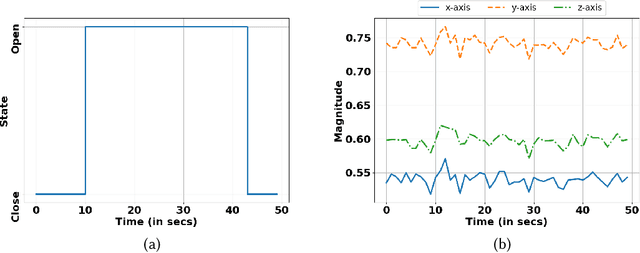

Efficient human activity recognition (HAR) using sensor data needs a significant volume of annotated data. The growing volume of unlabelled sensor data has challenged conventional practices for gathering HAR annotations with human-in-the-loop approaches, often leading to the collection of shallower annotations. These shallower annotations ignore the fine-grained micro-activities that constitute any complex activities of daily living (ADL). Understanding this, we, in this paper, first analyze this lack of granular annotations from available pre-annotated datasets to understand the practical inconsistencies and also perform a detailed survey to look into the human perception surrounding annotations. Drawing motivations from these, we next develop the framework AmicroN that can automatically generate micro-activity annotations using locomotive signatures and the available coarse-grain macro-activity labels. In the backend, AmicroN applies change-point detection followed by zero-shot learning with activity embeddings to identify the unseen micro-activities in an unsupervised manner. Rigorous evaluation on publicly available datasets shows that AmicroN can accurately generate micro-activity annotations with a median F1-score of >0.75. Additionally, we also show that AmicroN can be used in a plug-and-play manner with Large Language Models (LLMs) to obtain the micro-activity labels, thus making it more practical for realistic applications.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge