AEROBLADE: Training-Free Detection of Latent Diffusion Images Using Autoencoder Reconstruction Error
Paper and Code
Jan 31, 2024
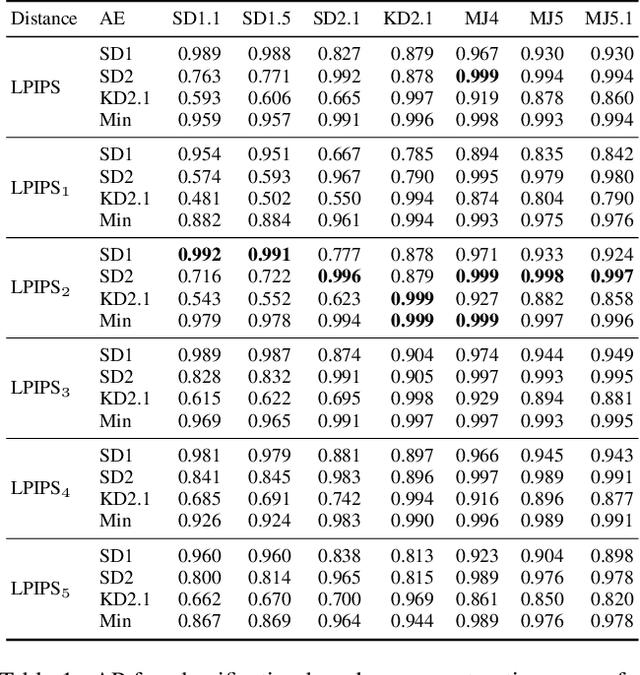
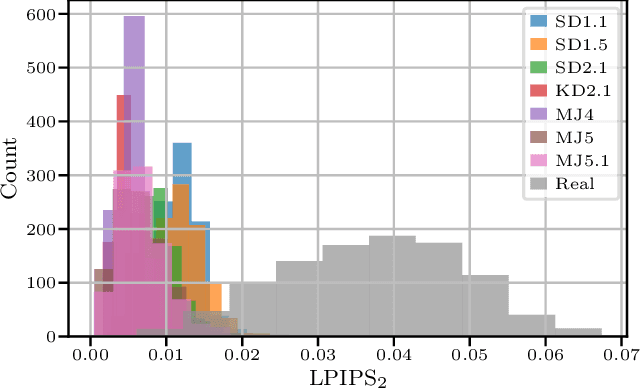
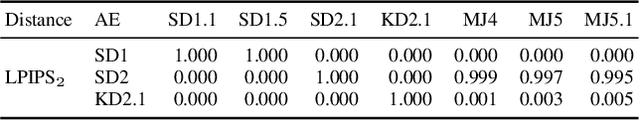
With recent text-to-image models, anyone can generate deceptively realistic images with arbitrary contents, fueling the growing threat of visual disinformation. A key enabler for generating high-resolution images with low computational cost has been the development of latent diffusion models (LDMs). In contrast to conventional diffusion models, LDMs perform the denoising process in the low-dimensional latent space of a pre-trained autoencoder (AE) instead of the high-dimensional image space. Despite their relevance, the forensic analysis of LDMs is still in its infancy. In this work we propose AEROBLADE, a novel detection method which exploits an inherent component of LDMs: the AE used to transform images between image and latent space. We find that generated images can be more accurately reconstructed by the AE than real images, allowing for a simple detection approach based on the reconstruction error. Most importantly, our method is easy to implement and does not require any training, yet nearly matches the performance of detectors that rely on extensive training. We empirically demonstrate that AEROBLADE is effective against state-of-the-art LDMs including Stable Diffusion and Midjourney. Beyond detection, our approach allows for the qualitative analysis of images, which can be leveraged for identifying inpainted regions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge