Adversarially Robust Submodular Maximization under Knapsack Constraints
Paper and Code
May 07, 2019
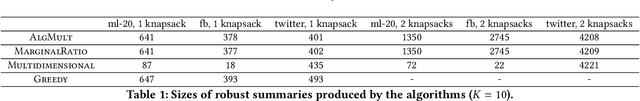
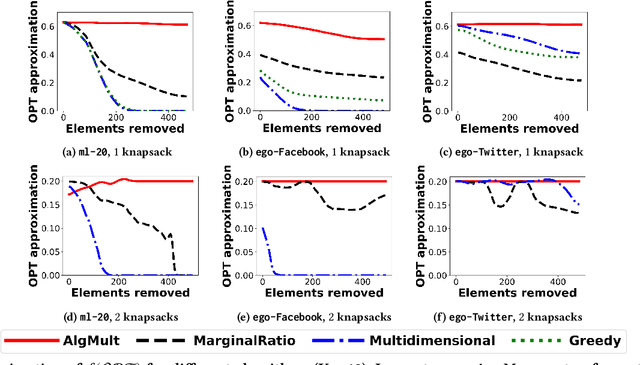
We propose the first adversarially robust algorithm for monotone submodular maximization under single and multiple knapsack constraints with scalable implementations in distributed and streaming settings. For a single knapsack constraint, our algorithm outputs a robust summary of almost optimal (up to polylogarithmic factors) size, from which a constant-factor approximation to the optimal solution can be constructed. For multiple knapsack constraints, our approximation is within a constant-factor of the best known non-robust solution. We evaluate the performance of our algorithms by comparison to natural robustifications of existing non-robust algorithms under two objectives: 1) dominating set for large social network graphs from Facebook and Twitter collected by the Stanford Network Analysis Project (SNAP), 2) movie recommendations on a dataset from MovieLens. Experimental results show that our algorithms give the best objective for a majority of the inputs and show strong performance even compared to offline algorithms that are given the set of removals in advance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge