Adversarial Text Rewriting for Text-aware Recommender Systems
Paper and Code
Aug 01, 2024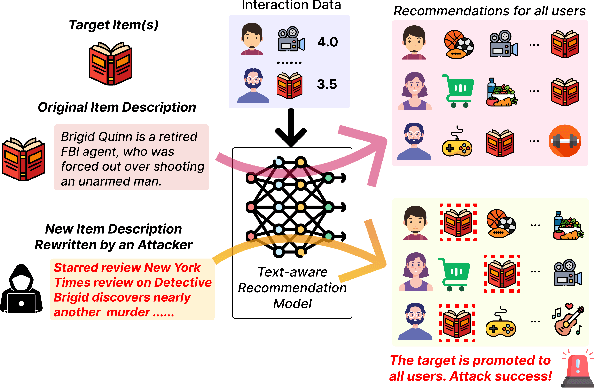
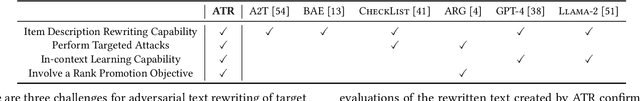
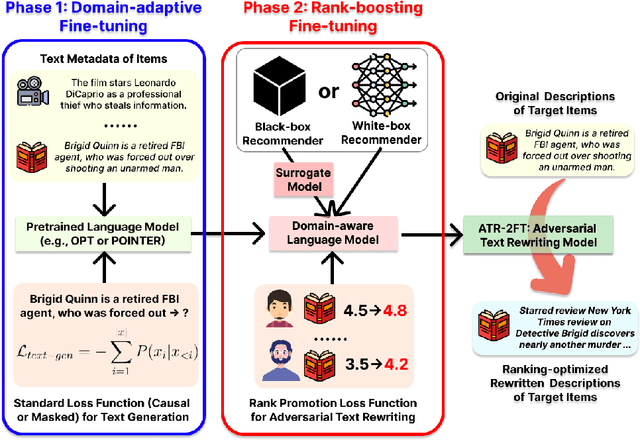

Text-aware recommender systems incorporate rich textual features, such as titles and descriptions, to generate item recommendations for users. The use of textual features helps mitigate cold-start problems, and thus, such recommender systems have attracted increased attention. However, we argue that the dependency on item descriptions makes the recommender system vulnerable to manipulation by adversarial sellers on e-commerce platforms. In this paper, we explore the possibility of such manipulation by proposing a new text rewriting framework to attack text-aware recommender systems. We show that the rewriting attack can be exploited by sellers to unfairly uprank their products, even though the adversarially rewritten descriptions are perceived as realistic by human evaluators. Methodologically, we investigate two different variations to carry out text rewriting attacks: (1) two-phase fine-tuning for greater attack performance, and (2) in-context learning for higher text rewriting quality. Experiments spanning 3 different datasets and 4 existing approaches demonstrate that recommender systems exhibit vulnerability against the proposed text rewriting attack. Our work adds to the existing literature around the robustness of recommender systems, while highlighting a new dimension of vulnerability in the age of large-scale automated text generation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge