Adversarial Radar Inference: Inverse Tracking, Identifying Cognition and Designing Smart Interference
Paper and Code
Aug 01, 2020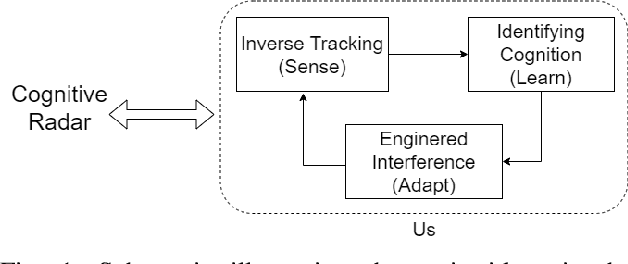
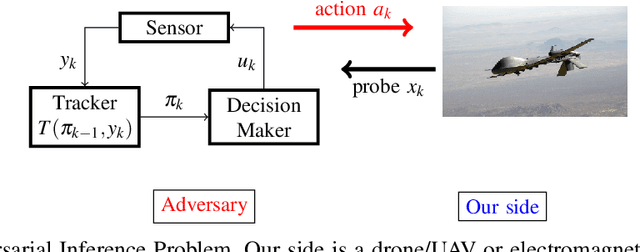
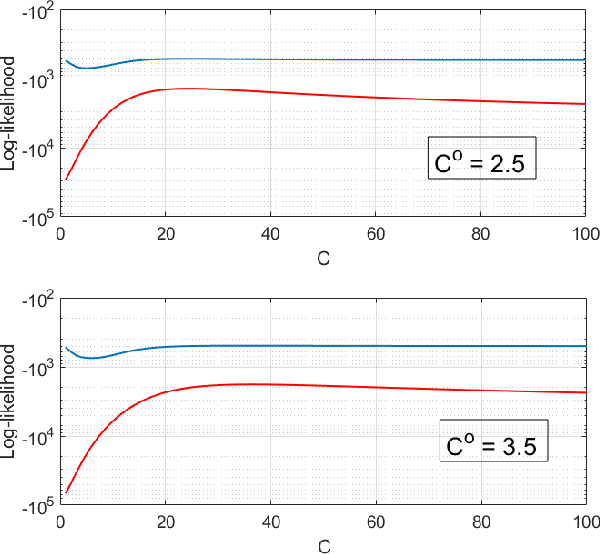
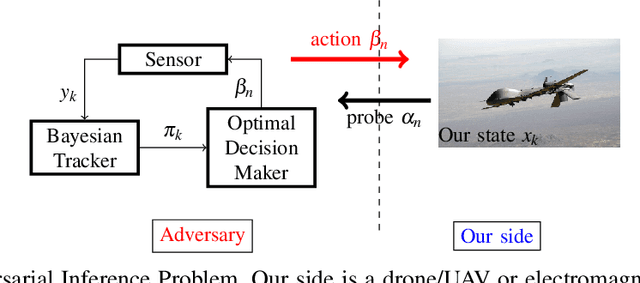
This paper considers three inter-related adversarial inference problems involving cognitive radars. We first discuss inverse tracking of the radar to estimate the adversary's estimate of us based on the radar's actions and calibrate the radar's sensing accuracy. Second, using revealed preference from microeconomics, we formulate a non-parametric test to identify if the cognitive radar is a constrained utility maximizer with signal processing constraints. We consider two radar functionalities, namely, beam allocation and waveform design, with respect to which the cognitive radar is assumed to maximize its utility and construct a set-valued estimator for the radar's utility function. Finally, we discuss how to engineer interference at the physical layer level to confuse the radar which forces it to change its transmit waveform. The levels of abstraction range from smart interference design based on Wiener filters (at the pulse/waveform level), inverse Kalman filters at the tracking level and revealed preferences for identifying utility maximization at the systems level.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge