Adversarial Plannning
Paper and Code
May 01, 2022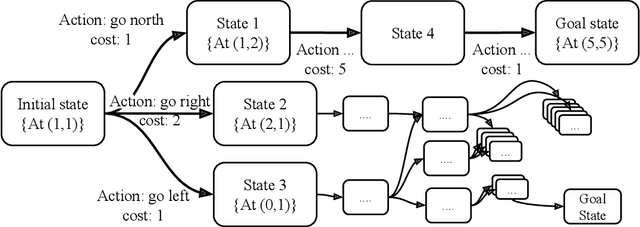
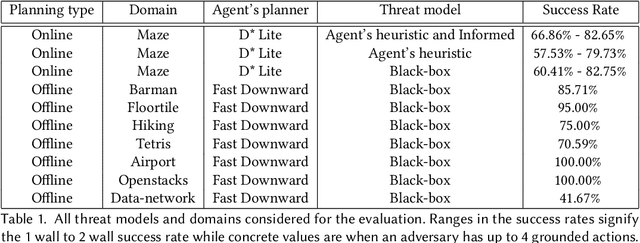
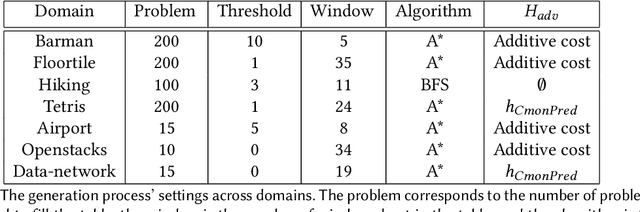
Planning algorithms are used in computational systems to direct autonomous behavior. In a canonical application, for example, planning for autonomous vehicles is used to automate the static or continuous planning towards performance, resource management, or functional goals (e.g., arriving at the destination, managing fuel fuel consumption). Existing planning algorithms assume non-adversarial settings; a least-cost plan is developed based on available environmental information (i.e., the input instance). Yet, it is unclear how such algorithms will perform in the face of adversaries attempting to thwart the planner. In this paper, we explore the security of planning algorithms used in cyber- and cyber-physical systems. We present two $\textit{adversarial planning}$ algorithms-one static and one adaptive-that perturb input planning instances to maximize cost (often substantially so). We evaluate the performance of the algorithms against two dominant planning algorithms used in commercial applications (D* Lite and Fast Downward) and show both are vulnerable to extremely limited adversarial action. Here, experiments show that an adversary is able to increase plan costs in 66.9% of instances by only removing a single action from the actions space (D* Lite) and render 70% of instances from an international planning competition unsolvable by removing only three actions (Fast Forward). Finally, we show that finding an optimal perturbation in any search-based planning system is NP-hard.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge