Adversarial Light Projection Attacks on Face Recognition Systems: A Feasibility Study
Paper and Code
Apr 17, 2020
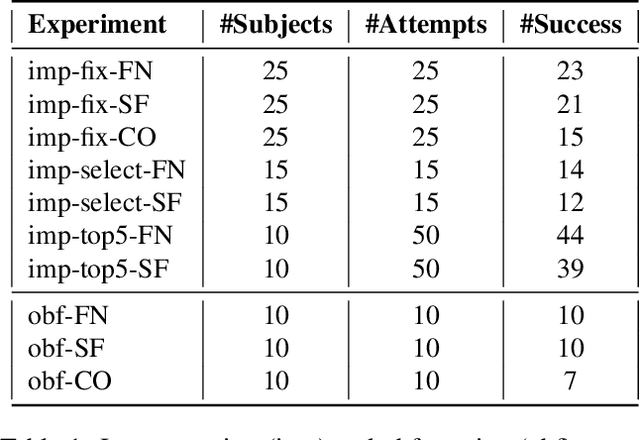

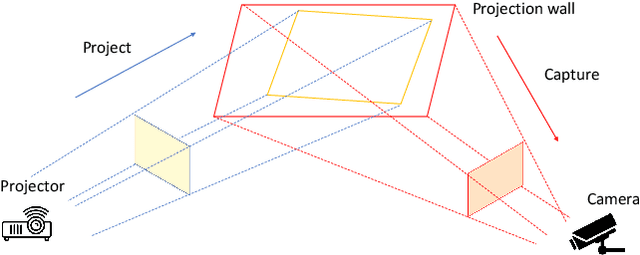
Deep learning-based systems have been shown to be vulnerable to adversarial attacks in both digital and physical domains. While feasible, digital attacks have limited applicability in attacking deployed systems, including face recognition systems, where an adversary typically has access to the input and not the transmission channel. In such setting, physical attacks that directly provide a malicious input through the input channel pose a bigger threat. We investigate the feasibility of conducting real-time physical attacks on face recognition systems using adversarial light projections. A setup comprising a commercially available web camera and a projector is used to conduct the attack. The adversary uses a transformation-invariant adversarial pattern generation method to generate a digital adversarial pattern using one or more images of the target available to the adversary. The digital adversarial pattern is then projected onto the adversary's face in the physical domain to either impersonate a target (impersonation) or evade recognition (obfuscation). We conduct preliminary experiments using two open-source and one commercial face recognition system on a pool of 50 subjects. Our experimental results demonstrate the vulnerability of face recognition systems to light projection attacks in both white-box and black-box attack settings.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge