Advanced Framework for Animal Sound Classification With Features Optimization
Paper and Code
Jul 03, 2024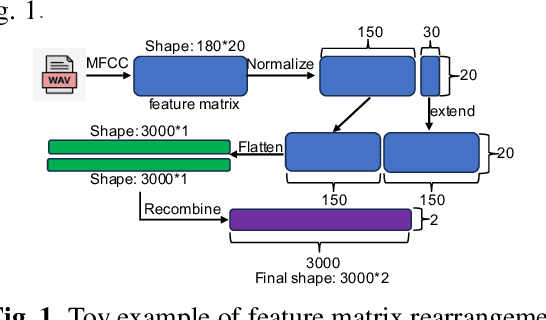
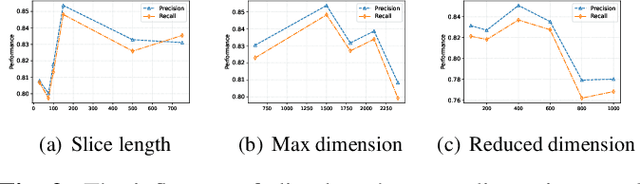
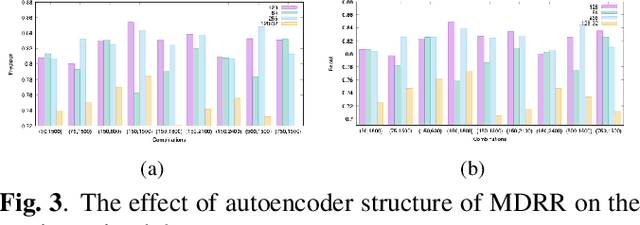
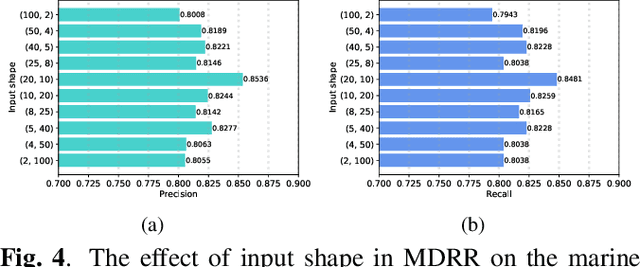
The automatic classification of animal sounds presents an enduring challenge in bioacoustics, owing to the diverse statistical properties of sound signals, variations in recording equipment, and prevalent low Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR) conditions. Deep learning models like Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) and Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) have excelled in human speech recognition but have not been effectively tailored to the intricate nature of animal sounds, which exhibit substantial diversity even within the same domain. We propose an automated classification framework applicable to general animal sound classification. Our approach first optimizes audio features from Mel-frequency cepstral coefficients (MFCC) including feature rearrangement and feature reduction. It then uses the optimized features for the deep learning model, i.e., an attention-based Bidirectional LSTM (Bi-LSTM), to extract deep semantic features for sound classification. We also contribute an animal sound benchmark dataset encompassing oceanic animals and birds1. Extensive experimentation with real-world datasets demonstrates that our approach consistently outperforms baseline methods by over 25% in precision, recall, and accuracy, promising advancements in animal sound classification.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge