Adjusting for Chance Clustering Comparison Measures
Paper and Code
Dec 03, 2015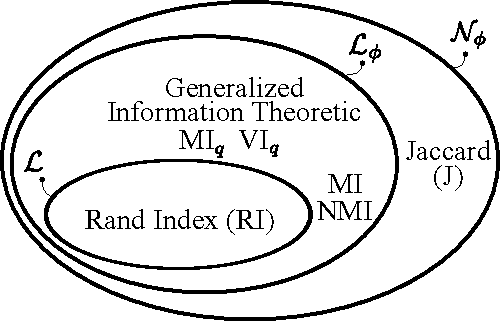
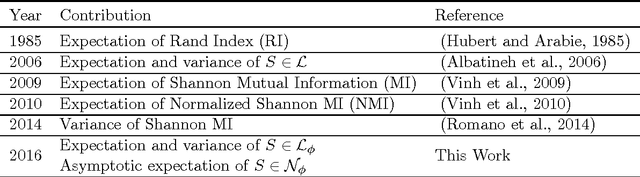
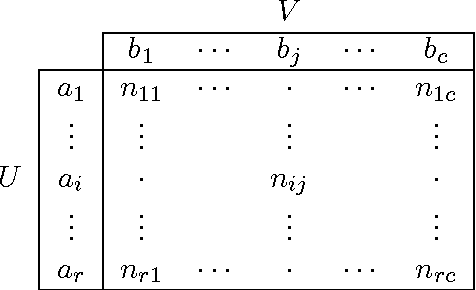
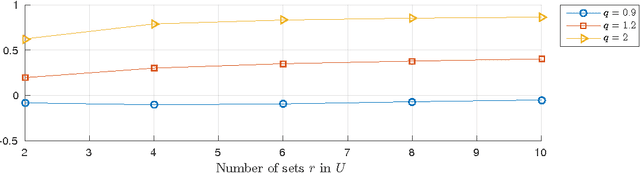
Adjusted for chance measures are widely used to compare partitions/clusterings of the same data set. In particular, the Adjusted Rand Index (ARI) based on pair-counting, and the Adjusted Mutual Information (AMI) based on Shannon information theory are very popular in the clustering community. Nonetheless it is an open problem as to what are the best application scenarios for each measure and guidelines in the literature for their usage are sparse, with the result that users often resort to using both. Generalized Information Theoretic (IT) measures based on the Tsallis entropy have been shown to link pair-counting and Shannon IT measures. In this paper, we aim to bridge the gap between adjustment of measures based on pair-counting and measures based on information theory. We solve the key technical challenge of analytically computing the expected value and variance of generalized IT measures. This allows us to propose adjustments of generalized IT measures, which reduce to well known adjusted clustering comparison measures as special cases. Using the theory of generalized IT measures, we are able to propose the following guidelines for using ARI and AMI as external validation indices: ARI should be used when the reference clustering has large equal sized clusters; AMI should be used when the reference clustering is unbalanced and there exist small clusters.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge