AdaptiVocab: Enhancing LLM Efficiency in Focused Domains through Lightweight Vocabulary Adaptation
Paper and Code
Mar 25, 2025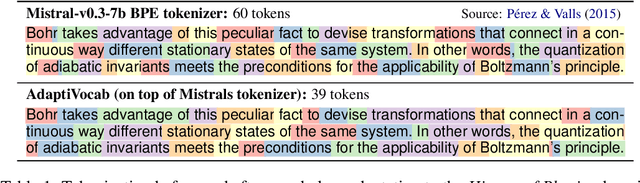
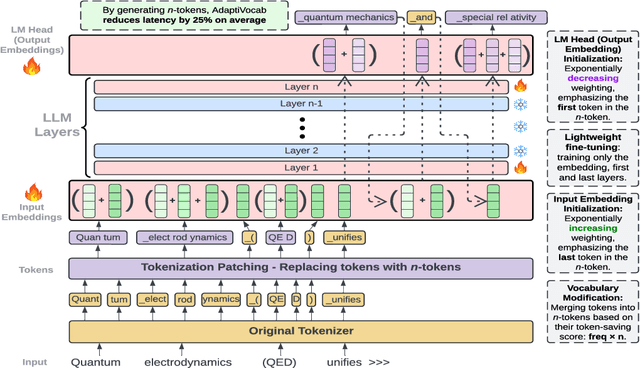
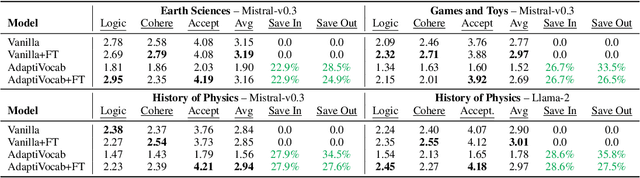
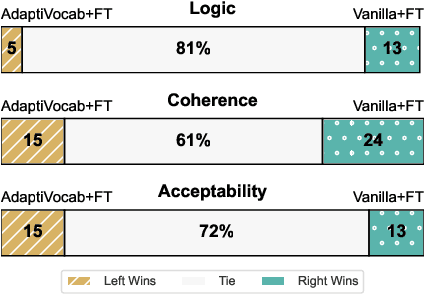
Large Language Models (LLMs) have shown impressive versatility as general purpose models. However, their broad applicability comes at a high-cost computational overhead, particularly in auto-regressive decoding where each step requires a forward pass. In domain-specific settings, general-purpose capabilities are unnecessary and can be exchanged for efficiency. In this work, we take a novel perspective on domain adaptation, reducing latency and computational costs by adapting the vocabulary to focused domains of interest. We introduce AdaptiVocab, an end-to-end approach for vocabulary adaptation, designed to enhance LLM efficiency in low-resource domains. AdaptiVocab can be applied to any tokenizer and architecture, modifying the vocabulary by replacing tokens with domain-specific n-gram-based tokens, thereby reducing the number of tokens required for both input processing and output generation. AdaptiVocab initializes new n-token embeddings using an exponentially weighted combination of existing embeddings and employs a lightweight fine-tuning phase that can be efficiently performed on a single GPU. We evaluate two 7B LLMs across three niche domains, assessing efficiency, generation quality, and end-task performance. Our results show that AdaptiVocab reduces token usage by over 25% without compromising performance
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge