Adaptive Elastic Training for Sparse Deep Learning on Heterogeneous Multi-GPU Servers
Paper and Code
Oct 13, 2021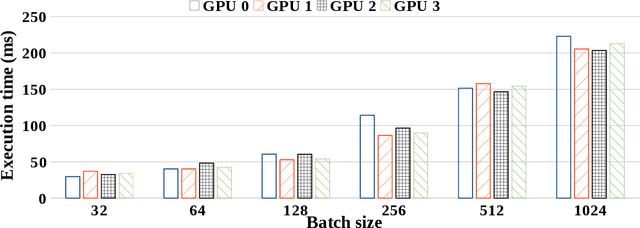

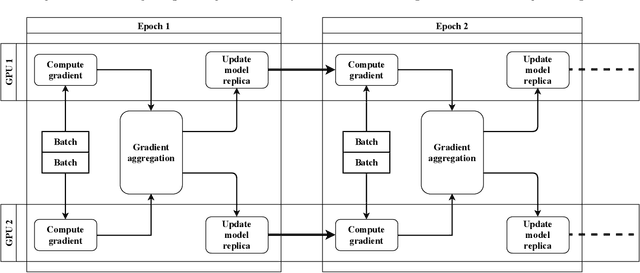
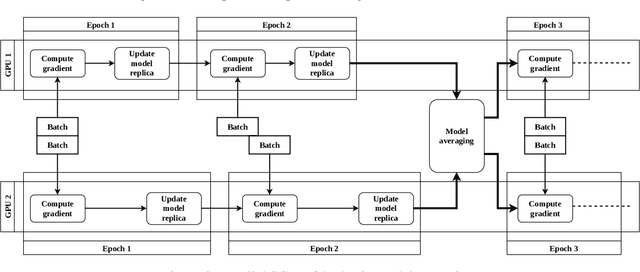
Motivated by extreme multi-label classification applications, we consider training deep learning models over sparse data in multi-GPU servers. The variance in the number of non-zero features across training batches and the intrinsic GPU heterogeneity combine to limit accuracy and increase the time to convergence. We address these challenges with Adaptive SGD, an adaptive elastic model averaging stochastic gradient descent algorithm for heterogeneous multi-GPUs that is characterized by dynamic scheduling, adaptive batch size scaling, and normalized model merging. Instead of statically partitioning batches to GPUs, batches are routed based on the relative processing speed. Batch size scaling assigns larger batches to the faster GPUs and smaller batches to the slower ones, with the goal to arrive at a steady state in which all the GPUs perform the same number of model updates. Normalized model merging computes optimal weights for every GPU based on the assigned batches such that the combined model achieves better accuracy. We show experimentally that Adaptive SGD outperforms four state-of-the-art solutions in time-to-accuracy and is scalable with the number of GPUs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge