Adaptive Correlated Monte Carlo for Contextual Categorical Sequence Generation
Paper and Code
Dec 31, 2019


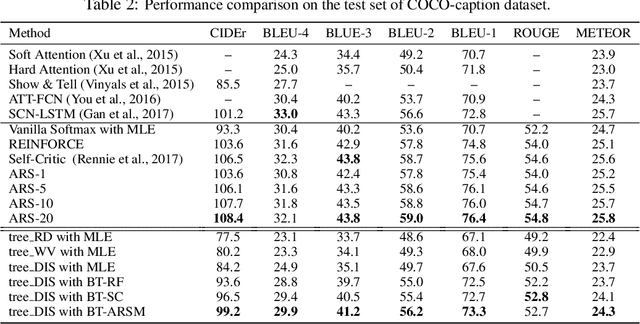
Sequence generation models are commonly refined with reinforcement learning over user-defined metrics. However, high gradient variance hinders the practical use of this method. To stabilize this method, we adapt to contextual generation of categorical sequences a policy gradient estimator, which evaluates a set of correlated Monte Carlo (MC) rollouts for variance control. Due to the correlation, the number of unique rollouts is random and adaptive to model uncertainty; those rollouts naturally become baselines for each other, and hence are combined to effectively reduce gradient variance. We also demonstrate the use of correlated MC rollouts for binary-tree softmax models, which reduce the high generation cost in large vocabulary scenarios by decomposing each categorical action into a sequence of binary actions. We evaluate our methods on both neural program synthesis and image captioning. The proposed methods yield lower gradient variance and consistent improvement over related baselines.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge