AdaMCT: Adaptive Mixture of CNN-Transformer for Sequential Recommendation
Paper and Code
May 19, 2022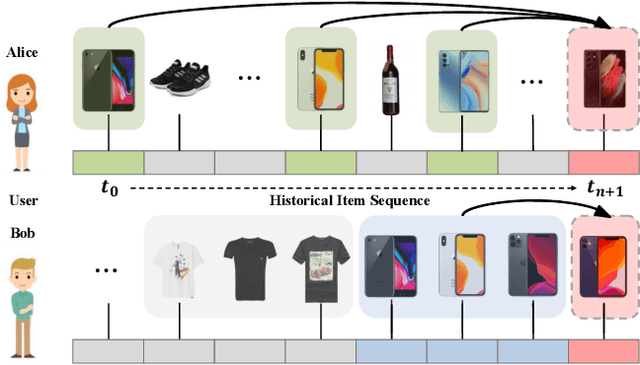
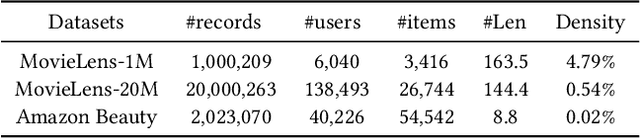
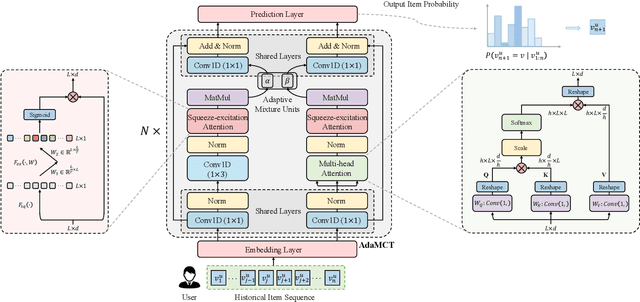
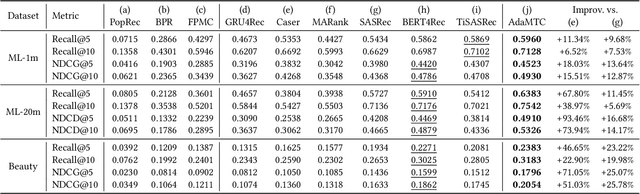
Sequential recommendation (SR) aims to model users' dynamic preferences from their historical interactions. Recently, Transformer and convolution neural networks (CNNs) have shown great success in learning representations for SR. Nevertheless, Transformer mainly focus on capturing content-based global interactions, while CNNs effectively exploit local features in practical recommendation scenarios. Thus, how to effectively aggregate CNNs and Transformer to model both \emph{local} and \emph{global} dependencies of historical item sequence still remains an open challenge and is rarely studied in SR. To this regard, we inject locality inductive bias into Transformer by combining its global attention mechanism with a local convolutional filter, and adaptively determine the mixing importance on a personalized basis through a module and layer-aware adaptive mixture units, named AdaMCT. Moreover, considering that softmax-based attention may encourage unimodal activation, we introduce the Squeeze-Excitation Attention (with sigmoid activation) into sequential recommendation to capture multiple relevant items (keys) simultaneously. Extensive experiments on three widely used benchmark datasets demonstrate that AdaMCT significantly outperforms the previous Transformer and CNNs-based models by an average of 18.46% and 60.85% respectively in terms of NDCG@5 and achieves state-of-the-art performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge