Activity Recognition for Autism Diagnosis
Paper and Code
Aug 25, 2021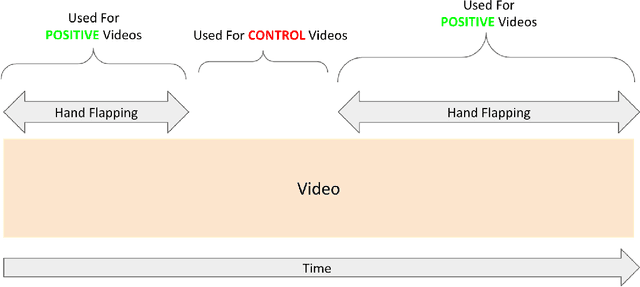
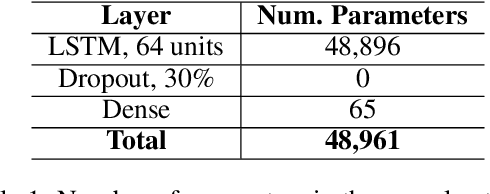

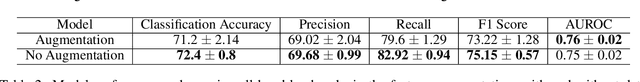
A formal autism diagnosis is an inefficient and lengthy process. Families often have to wait years before receiving a diagnosis for their child; some may not receive one at all due to this delay. One approach to this problem is to use digital technologies to detect the presence of behaviors related to autism, which in aggregate may lead to remote and automated diagnostics. One of the strongest indicators of autism is stimming, which is a set of repetitive, self-stimulatory behaviors such as hand flapping, headbanging, and spinning. Using computer vision to detect hand flapping is especially difficult due to the sparsity of public training data in this space and excessive shakiness and motion in such data. Our work demonstrates a novel method that overcomes these issues: we use hand landmark detection over time as a feature representation which is then fed into a Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) model. We achieve a validation accuracy and F1 Score of about 72% on detecting whether videos from the Self-Stimulatory Behaviour Dataset (SSBD) contain hand flapping or not. Our best model also predicts accurately on external videos we recorded of ourselves outside of the dataset it was trained on. This model uses less than 26,000 parameters, providing promise for fast deployment into ubiquitous and wearable digital settings for a remote autism diagnosis.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge