ActionCOMET: A Zero-shot Approach to Learn Image-specific Commonsense Concepts about Actions
Paper and Code
Oct 17, 2024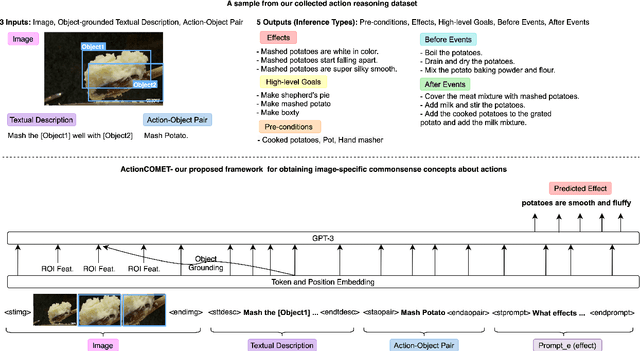
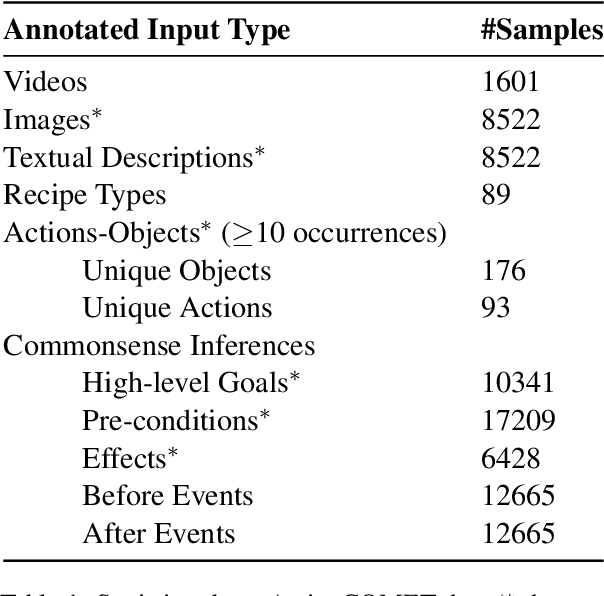
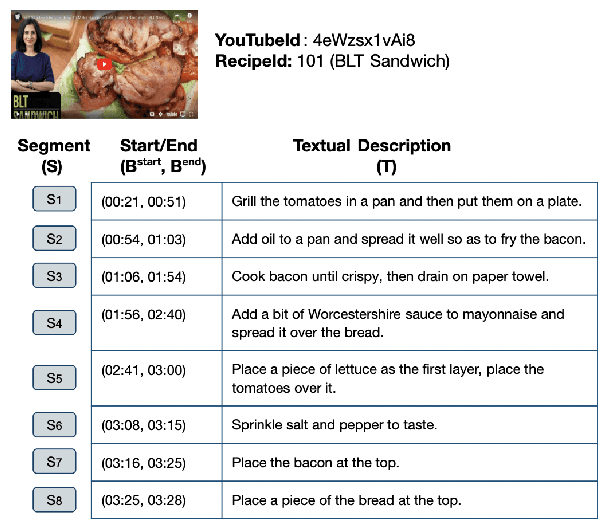
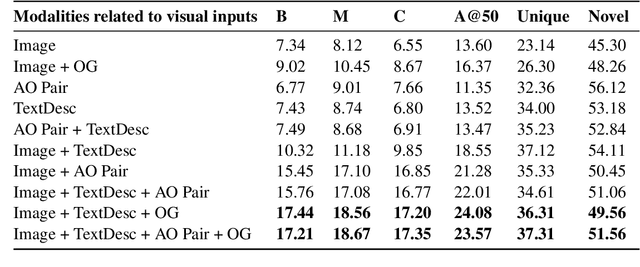
Humans observe various actions being performed by other humans (physically or in videos/images) and can draw a wide range of inferences about it beyond what they can visually perceive. Such inferences include determining the aspects of the world that make action execution possible (e.g. liquid objects can undergo pouring), predicting how the world will change as a result of the action (e.g. potatoes being golden and crispy after frying), high-level goals associated with the action (e.g. beat the eggs to make an omelet) and reasoning about actions that possibly precede or follow the current action (e.g. crack eggs before whisking or draining pasta after boiling). Similar reasoning ability is highly desirable in autonomous systems that would assist us in performing everyday tasks. To that end, we propose a multi-modal task to learn aforementioned concepts about actions being performed in images. We develop a dataset consisting of 8.5k images and 59.3k inferences about actions grounded in those images, collected from an annotated cooking-video dataset. We propose ActionCOMET, a zero-shot framework to discern knowledge present in language models specific to the provided visual input. We present baseline results of ActionCOMET over the collected dataset and compare them with the performance of the best existing VQA approaches.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge