Accelerating Graph Neural Networks via Edge Pruning for Power Allocation in Wireless Networks
Paper and Code
May 22, 2023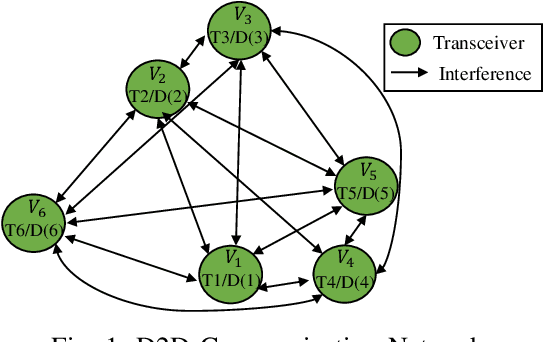
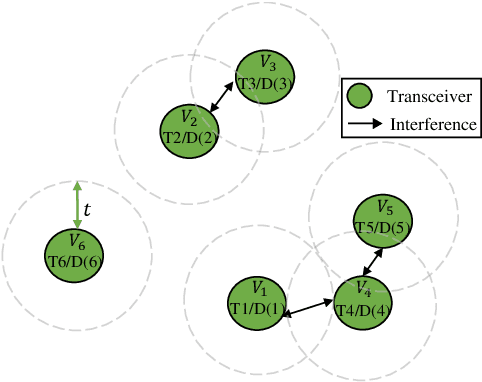
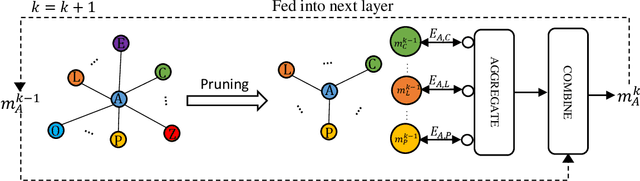
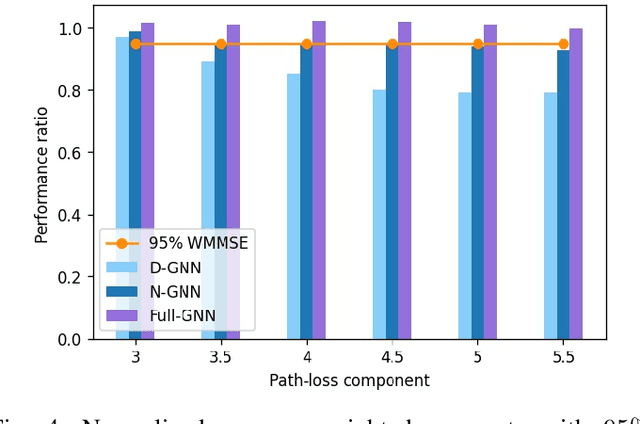
Neural Networks (GNNs) have recently emerged as a promising approach to tackling power allocation problems in wireless networks. Since unpaired transmitters and receivers are often spatially distant, the distanced-based threshold is proposed to reduce the computation time by excluding or including the channel state information in GNNs. In this paper, we are the first to introduce a neighbour-based threshold approach to GNNs to reduce the time complexity. Furthermore, we conduct a comprehensive analysis of both distance-based and neighbour-based thresholds and provide recommendations for selecting the appropriate value in different communication channel scenarios. We design the corresponding distance-based and neighbour-based Graph Neural Networks with the aim of allocating transmit powers to maximise the network throughput. Our results show that our proposed GNNs offer significant advantages in terms of reducing time complexity while preserving strong performance. Besides, we show that by choosing a suitable threshold, the time complexity is reduced from O(|V|^2) to O(|V|), where |V| is the total number of transceiver pairs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge