A Unified View of Localized Kernel Learning
Paper and Code
Mar 04, 2016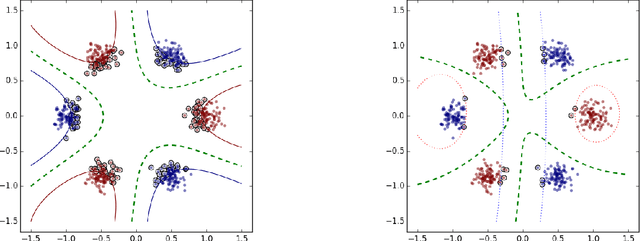
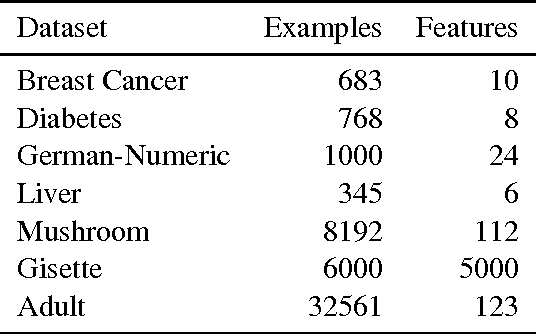
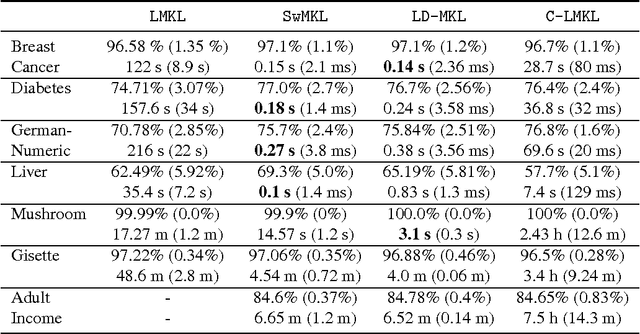
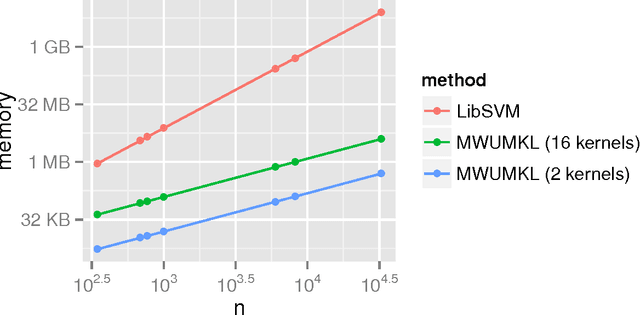
Multiple Kernel Learning, or MKL, extends (kernelized) SVM by attempting to learn not only a classifier/regressor but also the best kernel for the training task, usually from a combination of existing kernel functions. Most MKL methods seek the combined kernel that performs best over every training example, sacrificing performance in some areas to seek a global optimum. Localized kernel learning (LKL) overcomes this limitation by allowing the training algorithm to match a component kernel to the examples that can exploit it best. Several approaches to the localized kernel learning problem have been explored in the last several years. We unify many of these approaches under one simple system and design a new algorithm with improved performance. We also develop enhanced versions of existing algorithms, with an eye on scalability and performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge