A Unified Neural Coherence Model
Paper and Code
Sep 01, 2019
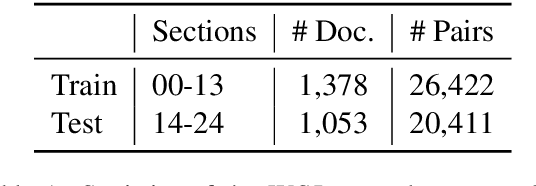
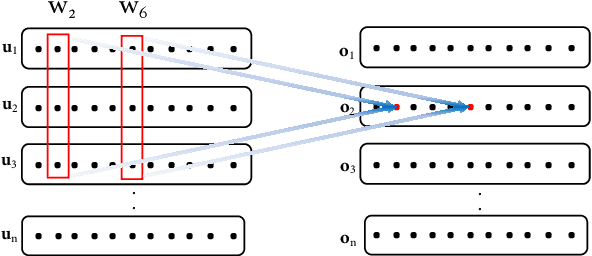
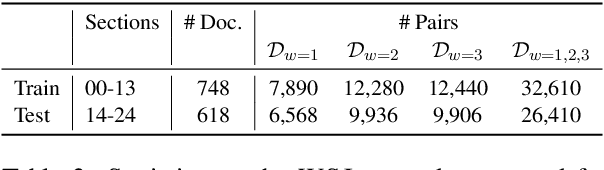
Recently, neural approaches to coherence modeling have achieved state-of-the-art results in several evaluation tasks. However, we show that most of these models often fail on harder tasks with more realistic application scenarios. In particular, the existing models underperform on tasks that require the model to be sensitive to local contexts such as candidate ranking in conversational dialogue and in machine translation. In this paper, we propose a unified coherence model that incorporates sentence grammar, inter-sentence coherence relations, and global coherence patterns into a common neural framework. With extensive experiments on local and global discrimination tasks, we demonstrate that our proposed model outperforms existing models by a good margin, and establish a new state-of-the-art.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge