A Survey on Deep Reinforcement Learning-based Approaches for Adaptation and Generalization
Paper and Code
Feb 17, 2022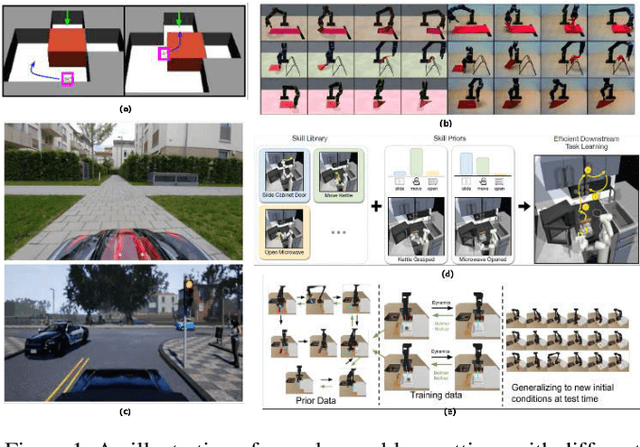
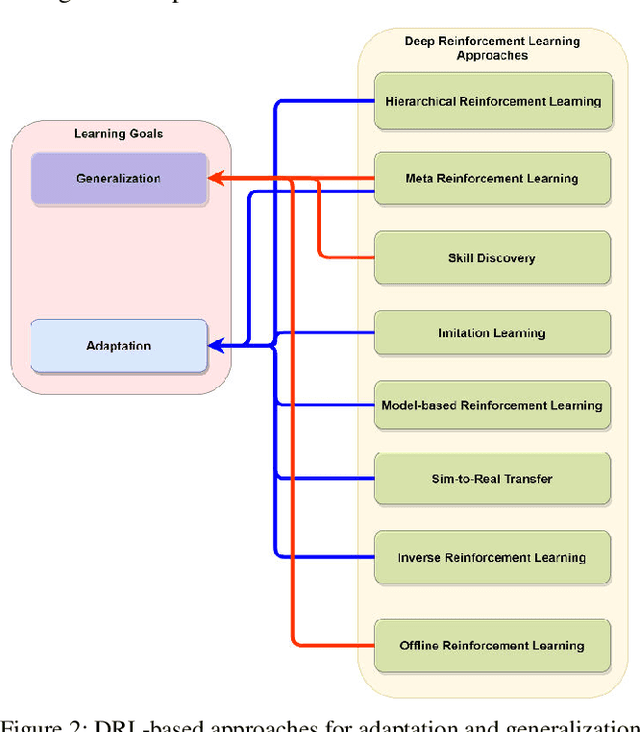
Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL) aims to create intelligent agents that can learn to solve complex problems efficiently in a real-world environment. Typically, two learning goals: adaptation and generalization are used for baselining DRL algorithm's performance on different tasks and domains. This paper presents a survey on the recent developments in DRL-based approaches for adaptation and generalization. We begin by formulating these goals in the context of task and domain. Then we review the recent works under those approaches and discuss future research directions through which DRL algorithms' adaptability and generalizability can be enhanced and potentially make them applicable to a broad range of real-world problems.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge