A Study on Self-Supervised Object Detection Pretraining
Paper and Code
Jul 09, 2022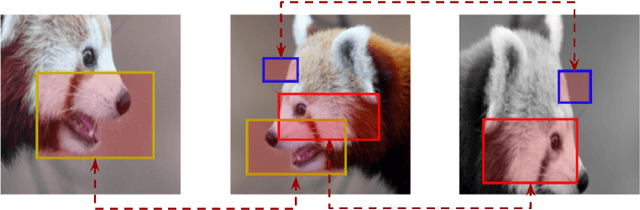
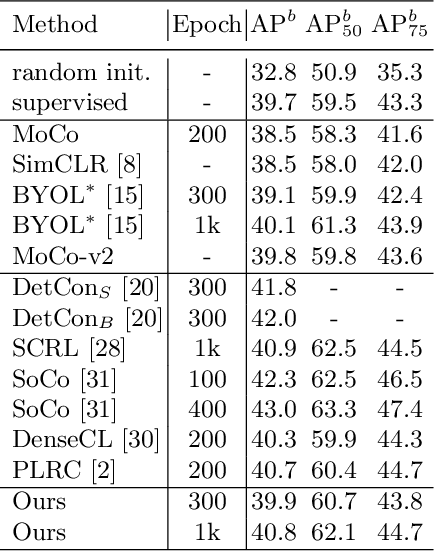
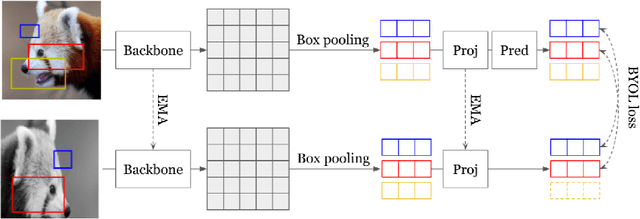
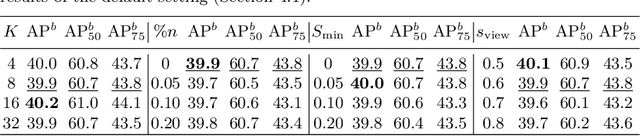
In this work, we study different approaches to self-supervised pretraining of object detection models. We first design a general framework to learn a spatially consistent dense representation from an image, by randomly sampling and projecting boxes to each augmented view and maximizing the similarity between corresponding box features. We study existing design choices in the literature, such as box generation, feature extraction strategies, and using multiple views inspired by its success on instance-level image representation learning techniques. Our results suggest that the method is robust to different choices of hyperparameters, and using multiple views is not as effective as shown for instance-level image representation learning. We also design two auxiliary tasks to predict boxes in one view from their features in the other view, by (1) predicting boxes from the sampled set by using a contrastive loss, and (2) predicting box coordinates using a transformer, which potentially benefits downstream object detection tasks. We found that these tasks do not lead to better object detection performance when finetuning the pretrained model on labeled data.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge