A structured regression approach for evaluating model performance across intersectional subgroups
Paper and Code
Jan 26, 2024
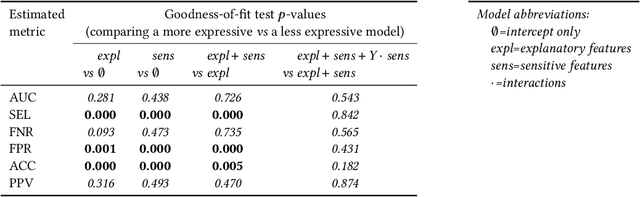

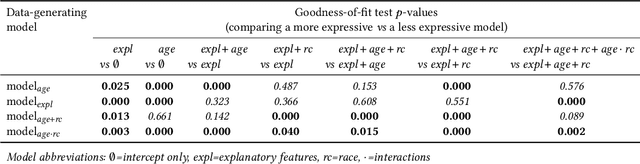
Disaggregated evaluation is a central task in AI fairness assessment, with the goal to measure an AI system's performance across different subgroups defined by combinations of demographic or other sensitive attributes. The standard approach is to stratify the evaluation data across subgroups and compute performance metrics separately for each group. However, even for moderately-sized evaluation datasets, sample sizes quickly get small once considering intersectional subgroups, which greatly limits the extent to which intersectional groups are considered in many disaggregated evaluations. In this work, we introduce a structured regression approach to disaggregated evaluation that we demonstrate can yield reliable system performance estimates even for very small subgroups. We also provide corresponding inference strategies for constructing confidence intervals and explore how goodness-of-fit testing can yield insight into the structure of fairness-related harms experienced by intersectional groups. We evaluate our approach on two publicly available datasets, and several variants of semi-synthetic data. The results show that our method is considerably more accurate than the standard approach, especially for small subgroups, and goodness-of-fit testing helps identify the key factors that drive differences in performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge