A Stability Analysis of Fine-Tuning a Pre-Trained Model
Paper and Code
Jan 24, 2023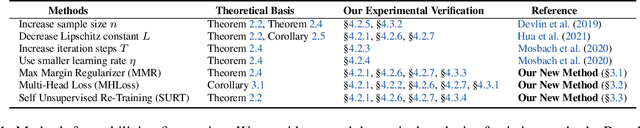
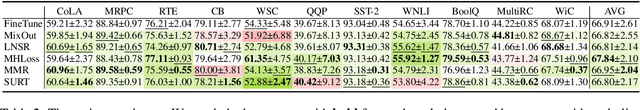
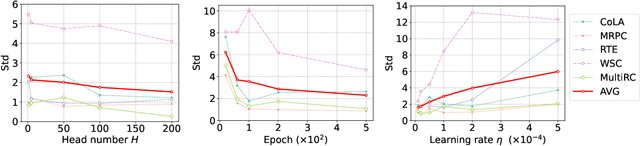
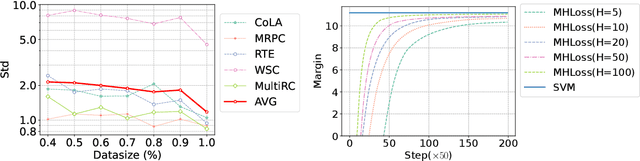
Fine-tuning a pre-trained model (such as BERT, ALBERT, RoBERTa, T5, GPT, etc.) has proven to be one of the most promising paradigms in recent NLP research. However, numerous recent works indicate that fine-tuning suffers from the instability problem, i.e., tuning the same model under the same setting results in significantly different performance. Many recent works have proposed different methods to solve this problem, but there is no theoretical understanding of why and how these methods work. In this paper, we propose a novel theoretical stability analysis of fine-tuning that focuses on two commonly used settings, namely, full fine-tuning and head tuning. We define the stability under each setting and prove the corresponding stability bounds. The theoretical bounds explain why and how several existing methods can stabilize the fine-tuning procedure. In addition to being able to explain most of the observed empirical discoveries, our proposed theoretical analysis framework can also help in the design of effective and provable methods. Based on our theory, we propose three novel strategies to stabilize the fine-tuning procedure, namely, Maximal Margin Regularizer (MMR), Multi-Head Loss (MHLoss), and Self Unsupervised Re-Training (SURT). We extensively evaluate our proposed approaches on 11 widely used real-world benchmark datasets, as well as hundreds of synthetic classification datasets. The experiment results show that our proposed methods significantly stabilize the fine-tuning procedure and also corroborate our theoretical analysis.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge