A Semi-supervised Learning Approach for B-line Detection in Lung Ultrasound Images
Paper and Code
Nov 30, 2022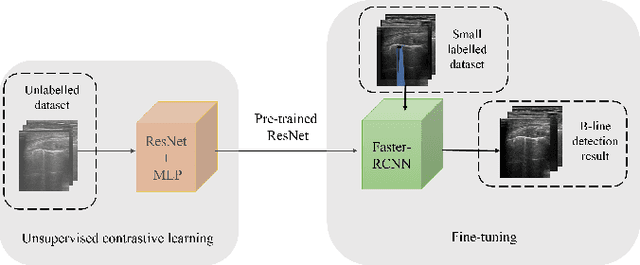
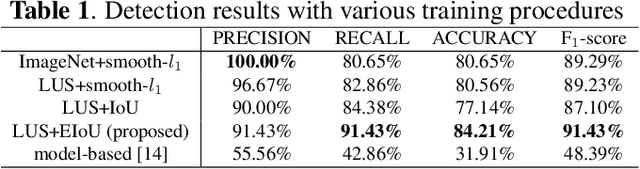
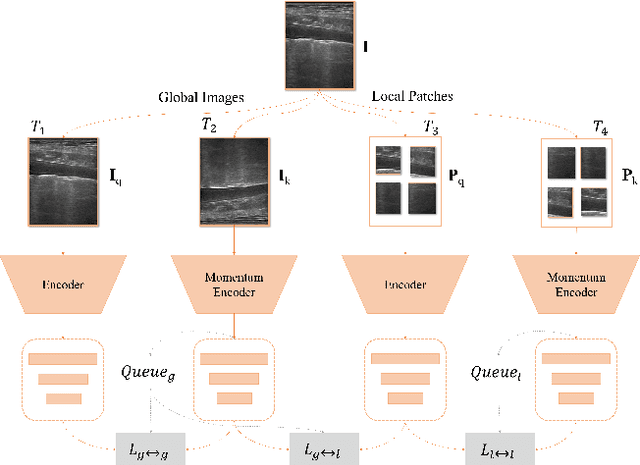
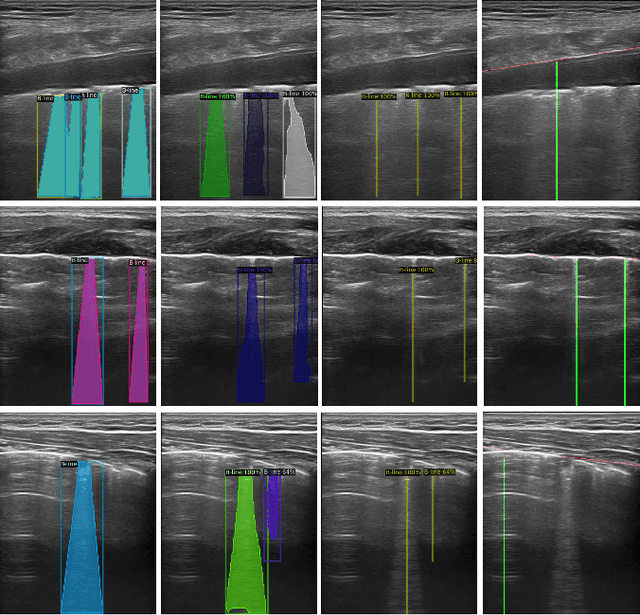
Studies have proved that the number of B-lines in lung ultrasound images has a strong statistical link to the amount of extravascular lung water, which is significant for hemodialysis treatment. Manual inspection of B-lines requires experts and is time-consuming, whilst modelling automation methods is currently problematic because of a lack of ground truth. Therefore, in this paper, we propose a novel semi-supervised learning method for the B-line detection task based on contrastive learning. Through multi-level unsupervised learning on unlabelled lung ultrasound images, the features of the artefacts are learnt. In the downstream task, we introduce a fine-tuning process on a small number of labelled images using the EIoU-based loss function. Apart from reducing the data labelling workload, the proposed method shows a superior performance to model-based algorithm with the recall of 91.43%, the accuracy of 84.21% and the F1 score of 91.43%.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge