A Rigorous Theory of Conditional Mean Embeddings
Paper and Code
Dec 16, 2019
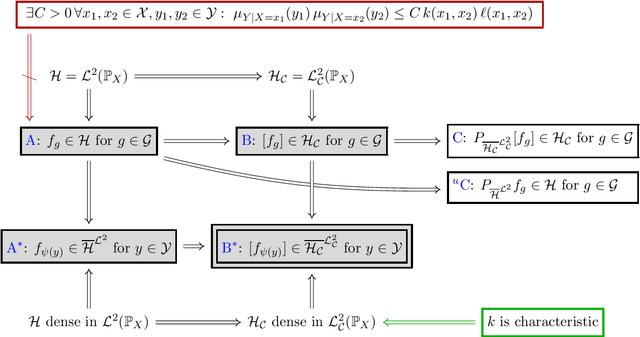
Conditional mean embeddings (CME) have proven themselves to be a powerful tool in many machine learning applications. They allow the efficient conditioning of probability distributions within the corresponding reproducing kernel Hilbert spaces (RKHSs) by providing a linear-algebraic relation for the kernel mean embeddings of the respective probability distributions. Both centered and uncentered covariance operators have been used to define CMEs in the existing literature. In this paper, we develop a mathematically rigorous theory for both variants, discuss the merits and problems of either, and significantly weaken the conditions for applicability of CMEs. In the course of this, we demonstrate a beautiful connection to Gaussian conditioning in Hilbert spaces.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge