A Radiomics Approach to Computer-Aided Diagnosis with Cardiac Cine-MRI
Paper and Code
Sep 25, 2019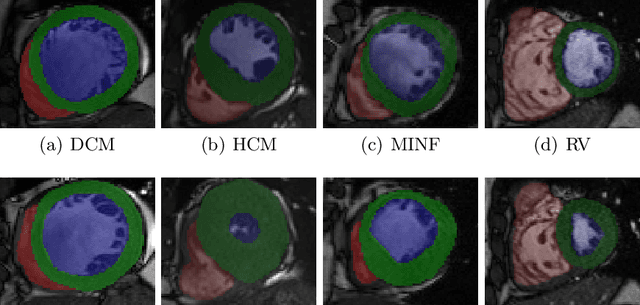
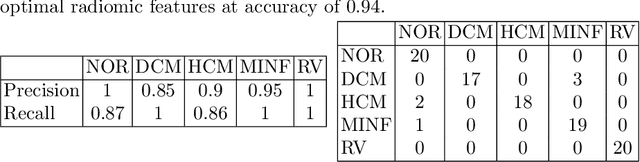
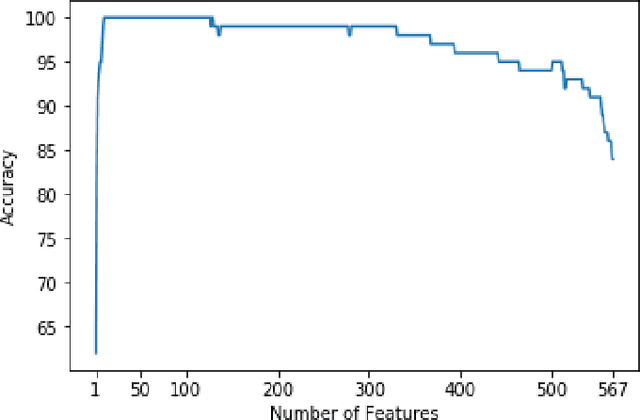
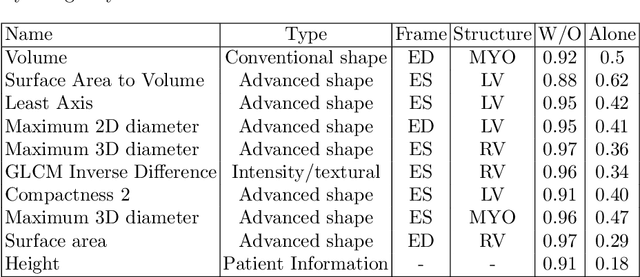
Use expert visualization or conventional clinical indices can lack accuracy for borderline classications. Advanced statistical approaches based on eigen-decomposition have been mostly concerned with shape and motion indices. In this paper, we present a new approach to identify CVDs from cine-MRI by estimating large pools of radiomic features (statistical, shape and textural features) encoding relevant changes in anatomical and image characteristics due to CVDs. The calculated cine-MRI radiomic features are assessed using sequential forward feature selection to identify the most relevant ones for given CVD classes (e.g. myocardial infarction, cardiomyopathy, abnormal right ventricle). Finally, advanced machine learning is applied to suitably integrate the selected radiomics for final multi-feature classification based on Support Vector Machines (SVMs). The proposed technique was trained and cross-validated using 100 cine-MRI cases corresponding to five different cardiac classes from the ACDC MICCAI 2017 challenge \footnote{https://www.creatis.insa-lyon.fr/Challenge/acdc/index.html}. All cases were correctly classified in this preliminary study, indicating potential of using large-scale radiomics for MRI-based diagnosis of CVDs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge