A preference learning framework for multiple criteria sorting with diverse additive value models and valued assignment examples
Paper and Code
Oct 12, 2019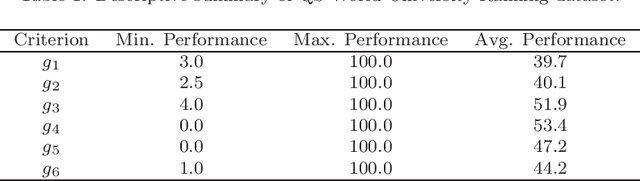
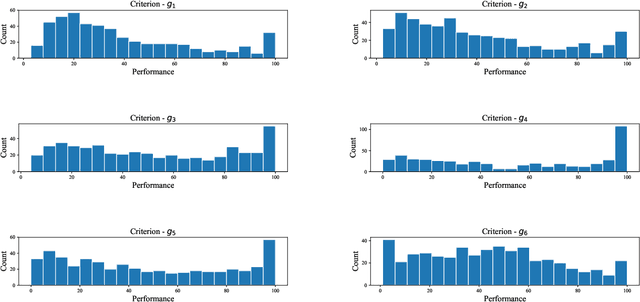
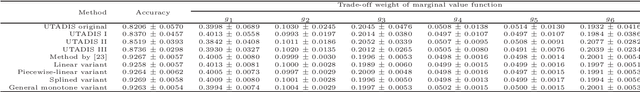
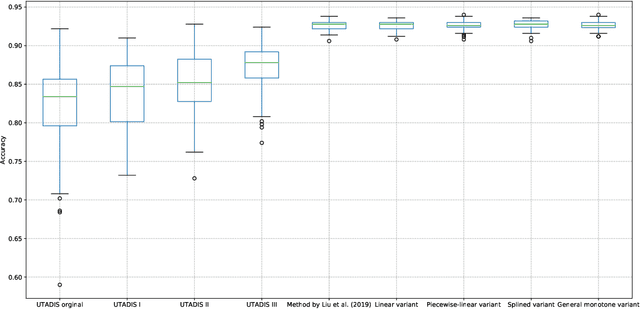
We present a preference learning framework for multiple criteria sorting. We consider sorting procedures applying an additive value model with diverse types of marginal value functions (including linear, piecewise-linear, splined, and general monotone ones) under a unified analytical framework. Differently from the existing sorting methods that infer a preference model from crisp decision examples, where each reference alternative is assigned to a unique class, our framework allows to consider valued assignment examples in which a reference alternative can be classified into multiple classes with respective credibility degrees. We propose an optimization model for constructing a preference model from such valued examples by maximizing the credible consistency among reference alternatives. To improve the predictive ability of the constructed model on new instances, we employ the regularization techniques. Moreover, to enhance the capability of addressing large-scale datasets, we introduce a state-of-the-art algorithm that is widely used in the machine learning community to solve the proposed optimization model in a computationally efficient way. Using the constructed additive value model, we determine both crisp and valued assignments for non-reference alternatives. Moreover, we allow the Decision Maker to prioritize importance of classes and give the method a flexibility to adjust classification performance across classes according to the specified priorities. The practical usefulness of the analytical framework is demonstrated on a real-world dataset by comparing it to several existing sorting methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge