A Possible Reason for why Data-Driven Beats Theory-Driven Computer Vision
Paper and Code
Sep 06, 2019
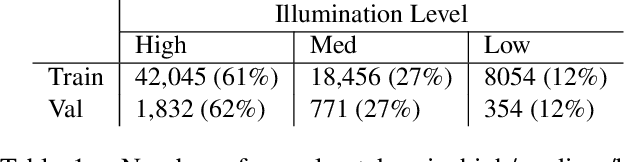
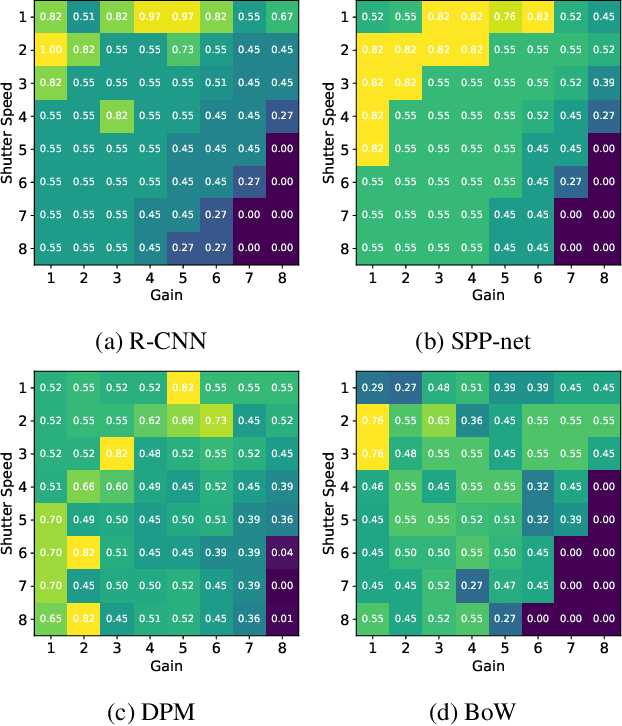

Why do some continue to wonder about the success and dominance of deep learning methods in computer vision and AI? Is it not enough that these methods provide practical solutions to many problems? Well no, it is not enough, at least for those who feel there should be a science that underpins all of this and that we should have a clear understanding of how this success was achieved. Here, this paper proposes that the dominance we are witnessing would not have been possible by the methods of deep learning alone: the tacit change has been the evolution of empirical practice in computer vision and AI over the past decades. We demonstrate this by examining the distribution of sensor settings in vision datasets and performance of both classic and deep learning algorithms under various camera settings. This reveals a strong mismatch between optimal performance ranges of classical theory-driven algorithms and sensor setting distributions in the common vision datasets, while data-driven models were trained for those datasets. The head-to-head comparisons between data-driven and theory-driven models were therefore unknowingly biased against the theory-driven models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge