A performance contextualization approach to validating camera models for robot simulation
Paper and Code
Aug 01, 2022
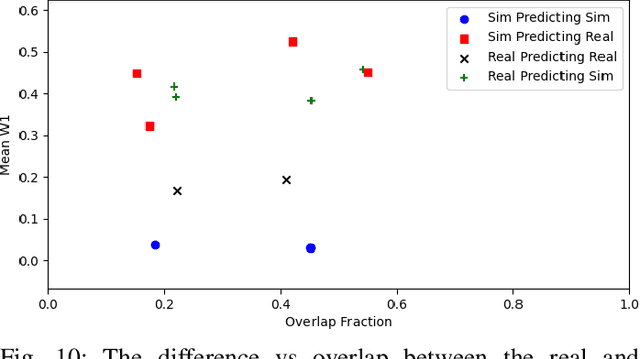

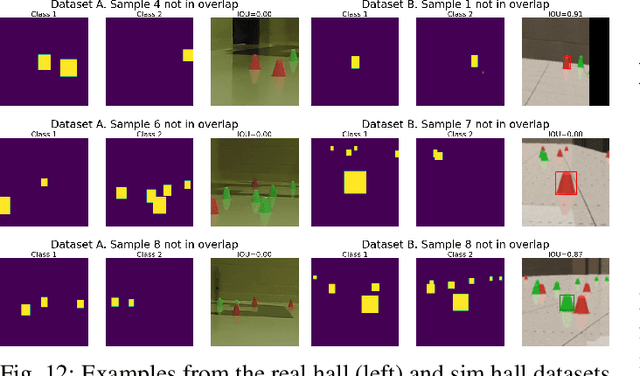
The focus of this contribution is on camera simulation as it comes into play in simulating autonomous robots for their virtual prototyping. We propose a camera model validation methodology based on the performance of a perception algorithm and the context in which the performance is measured. This approach is different than traditional validation of synthetic images, which is often done at a pixel or feature level, and tends to require matching pairs of synthetic and real images. Due to the high cost and constraints of acquiring paired images, the proposed approach is based on datasets that are not necessarily paired. Within a real and a simulated dataset, A and B, respectively, we find subsets Ac and Bc of similar content and judge, statistically, the perception algorithm's response to these similar subsets. This validation approach obtains a statistical measure of performance similarity, as well as a measure of similarity between the content of A and B. The methodology is demonstrated using images generated with Chrono::Sensor and a scaled autonomous vehicle, using an object detector as the perception algorithm. The results demonstrate the ability to quantify (i) differences between simulated and real data; (ii) the propensity of training methods to mitigate the sim-to-real gap; and (iii) the context overlap between two datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge