A Novel Markovian Framework for Integrating Absolute and Relative Ordinal Emotion Information
Paper and Code
Aug 10, 2021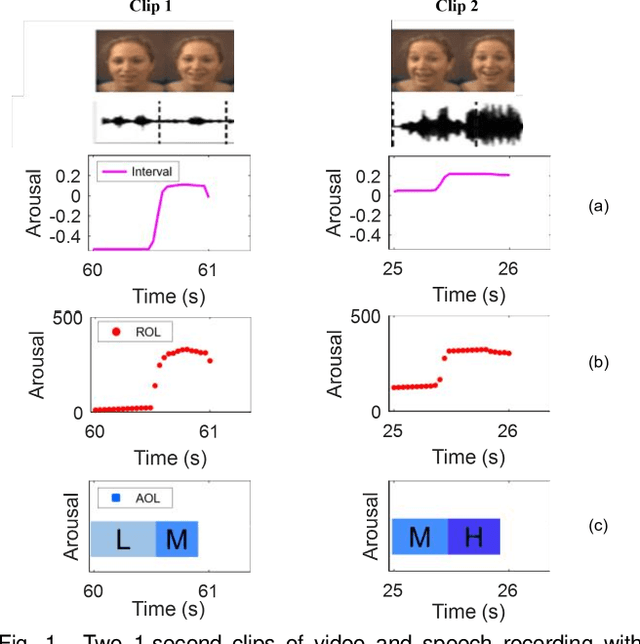
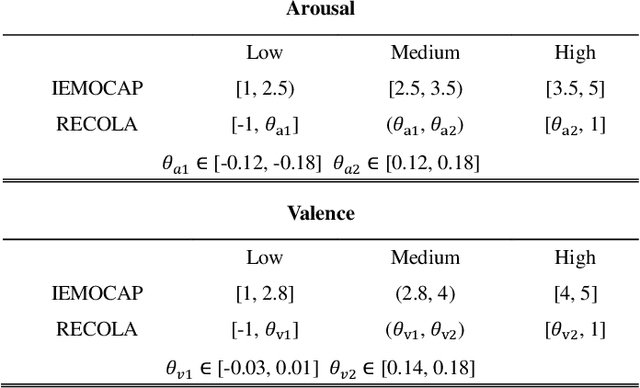
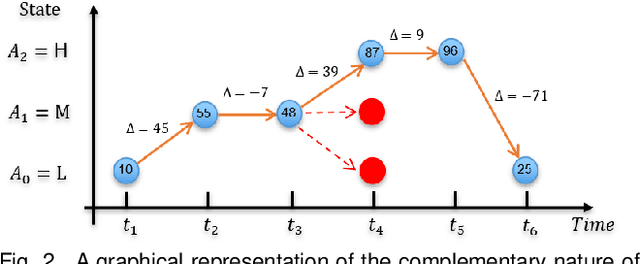
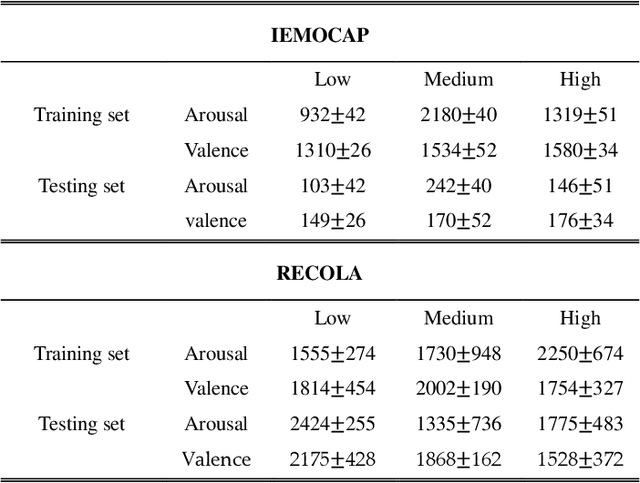
There is growing interest in affective computing for the representation and prediction of emotions along ordinal scales. However, the term ordinal emotion label has been used to refer to both absolute notions such as low or high arousal, as well as relation notions such as arousal is higher at one instance compared to another. In this paper, we introduce the terminology absolute and relative ordinal labels to make this distinction clear and investigate both with a view to integrate them and exploit their complementary nature. We propose a Markovian framework referred to as Dynamic Ordinal Markov Model (DOMM) that makes use of both absolute and relative ordinal information, to improve speech based ordinal emotion prediction. Finally, the proposed framework is validated on two speech corpora commonly used in affective computing, the RECOLA and the IEMOCAP databases, across a range of system configurations. The results consistently indicate that integrating relative ordinal information improves absolute ordinal emotion prediction.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge