A Novel Image Denoising Algorithm Using Concepts of Quantum Many-Body Theory
Paper and Code
Dec 16, 2021
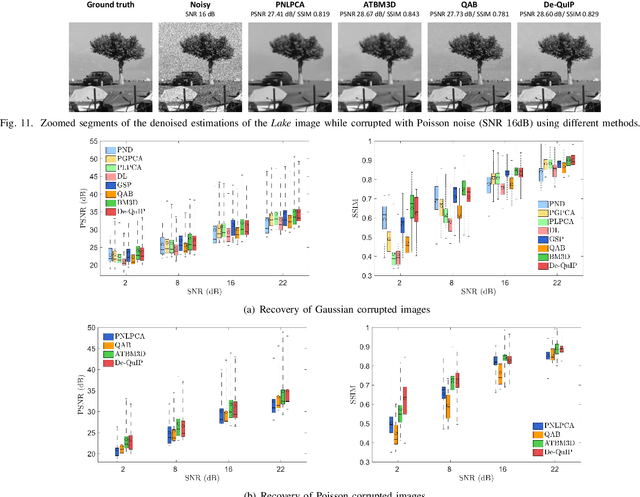
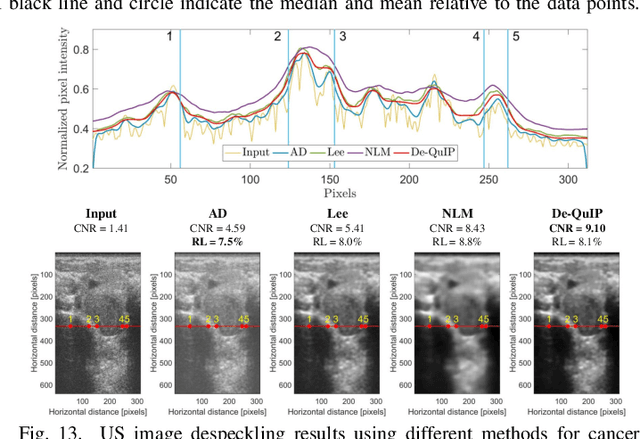

Sparse representation of real-life images is a very effective approach in imaging applications, such as denoising. In recent years, with the growth of computing power, data-driven strategies exploiting the redundancy within patches extracted from one or several images to increase sparsity have become more prominent. This paper presents a novel image denoising algorithm exploiting such an image-dependent basis inspired by the quantum many-body theory. Based on patch analysis, the similarity measures in a local image neighborhood are formalized through a term akin to interaction in quantum mechanics that can efficiently preserve the local structures of real images. The versatile nature of this adaptive basis extends the scope of its application to image-independent or image-dependent noise scenarios without any adjustment. We carry out a rigorous comparison with contemporary methods to demonstrate the denoising capability of the proposed algorithm regardless of the image characteristics, noise statistics and intensity. We illustrate the properties of the hyperparameters and their respective effects on the denoising performance, together with automated rules of selecting their values close to the optimal one in experimental setups with ground truth not available. Finally, we show the ability of our approach to deal with practical images denoising problems such as medical ultrasound image despeckling applications.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge