A Next Basket Recommendation Reality Check
Paper and Code
Sep 29, 2021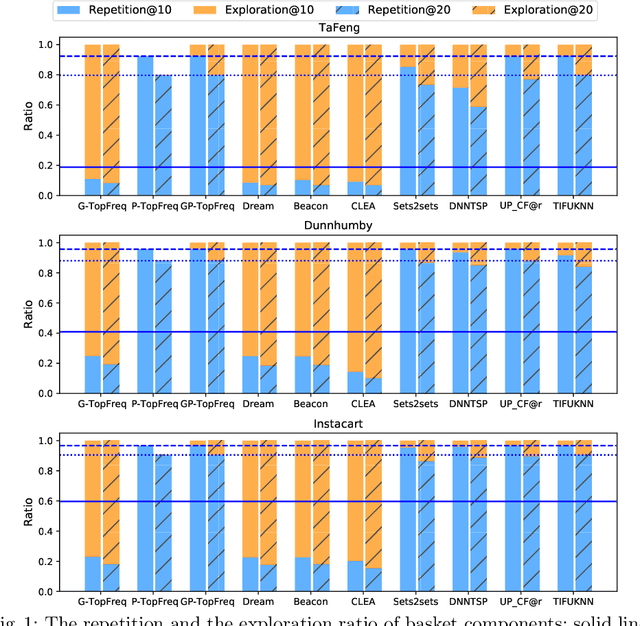
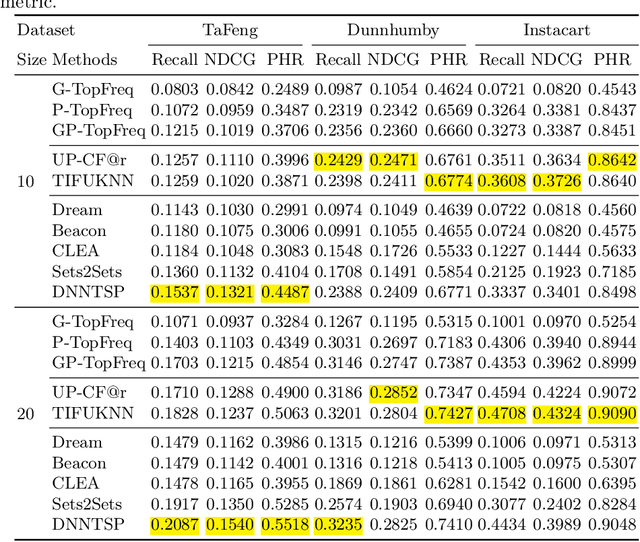
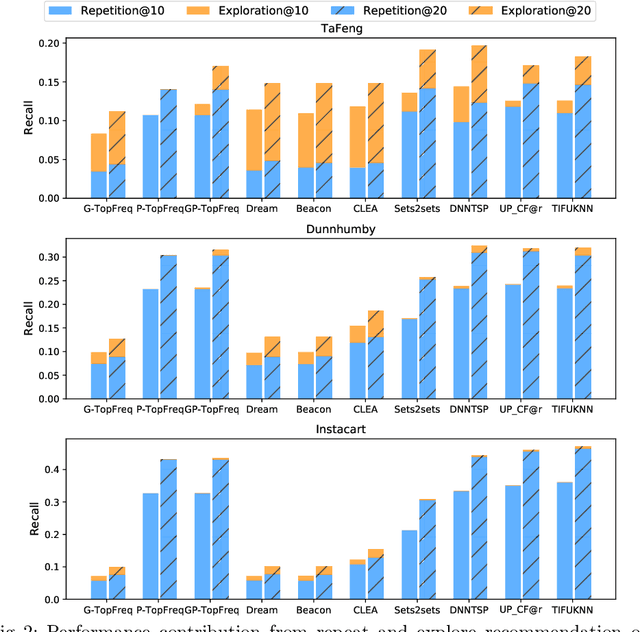
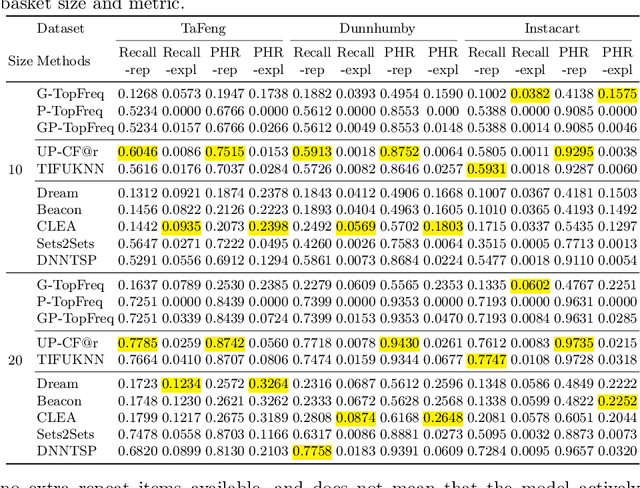
The goal of a next basket recommendation (NBR) system is to recommend items for the next basket for a user, based on the sequence of their prior baskets. Recently, a number of methods with complex modules have been proposed that claim state-of-the-art performance. They rarely look into the predicted basket and just provide intuitive reasons for the observed improvements, e.g., better representation, capturing intentions or relations, etc. We provide a novel angle on the evaluation of next basket recommendation methods, centered on the distinction between repetition and exploration: the next basket is typically composed of previously consumed items (i.e., repeat items) and new items (i.e, explore items). We propose a set of metrics that measure the repeat/explore ratio and performance of NBR models. Using these new metrics, we analyze state-of-the-art NBR models. The results of our analysis help to clarify the extent of the actual progress achieved by existing NBR methods as well as the underlying reasons for the improvements. Overall, our work sheds light on the evaluation problem of NBR and provides useful insights into the model design for this task.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge