A Multi-Orientation Analysis Approach to Retinal Vessel Tracking
Paper and Code
Dec 30, 2013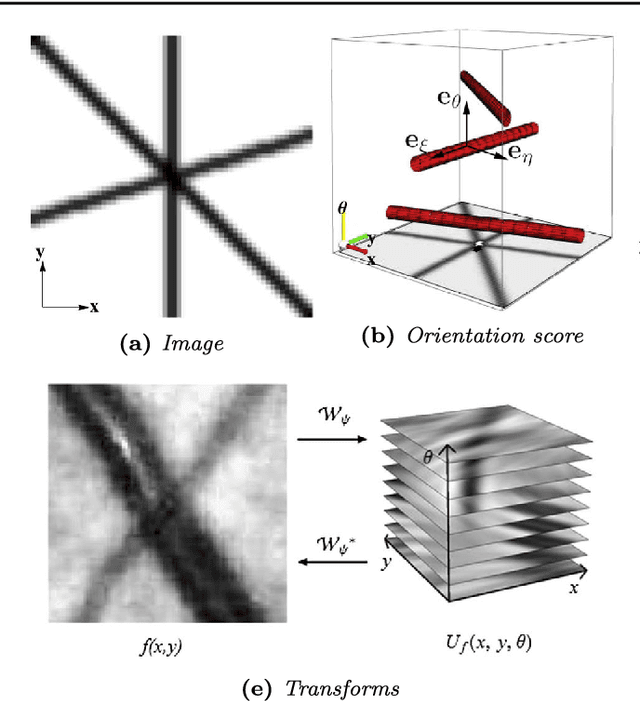


This paper presents a method for retinal vasculature extraction based on biologically inspired multi-orientation analysis. We apply multi-orientation analysis via so-called invertible orientation scores, modeling the cortical columns in the visual system of higher mammals. This allows us to generically deal with many hitherto complex problems inherent to vessel tracking, such as crossings, bifurcations, parallel vessels, vessels of varying widths and vessels with high curvature. Our approach applies tracking in invertible orientation scores via a novel geometrical principle for curve optimization in the Euclidean motion group SE(2). The method runs fully automatically and provides a detailed model of the retinal vasculature, which is crucial as a sound basis for further quantitative analysis of the retina, especially in screening applications.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge